
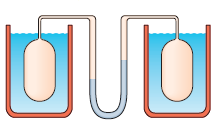
A gas thermometer is constructed of two gas-containing bulbs, each in a water bath. The pressure difference between the two bulbs is measured by a mercury manometer as shown. Appropriate reservoirs, not shown in the diagram in pressure when both baths are at the triple point of water. The pressure difference is \[120torr\] when one bath is at the triple point and the other is at the boiling point of water. It is \[90torr\] when one bath is at the triple point and the other is at an unknown temperature to be measured. What is the unknown temperature?

Answer
516.3k+ views
Hint: Usually thermometers are used to measure the temperature. So here also we will measure the unknown temperature of a gas thermometer constructed of two gas-containing bulbs, each in a water bath. The pressure differences are given for two conditions that are one bath is at the triple point and the other is at the boiling point of water, and one bath is at the triple point and the other is at an unknown temperature. With the help of pressure difference, we will measure the unknown temperature.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Let us consider, \[{T_L}\]-Temperature of the left-hand thermometer, and \[{P_L}\]-Pressure in the left-hand thermometer. Similarly, \[{T_R}\]-Temperature of the right-hand thermometer, and \[{P_R}\]-Pressure in the right-hand thermometer.
From the statement given in the problem, the pressure is the same in two thermometers when they are both at the triple point of water. We will take this pressure\[{P_3}\].
\[\dfrac{T}{P} = \dfrac{{{T_3}}}{{{P_3}}} \Rightarrow T = {T_3} \times \dfrac{P}{{{P_3}}}\] \[\left( {\therefore {T_3} = 273.16K} \right)\]-Triple point of water
The equation for both left and both thermometer
\[{T_L} = \left( {273.16K} \right) \times \dfrac{{{P_L}}}{{{P_3}}}\] and \[{T_R} = \left( {273.16K} \right) \times \dfrac{{{P_R}}}{{{P_3}}}\]
Subtract the second equation from the first equation
\[{T_L} - {T_R} = \left( {273.16K} \right) \times \left( {\dfrac{{{P_L} - {P_R}}}{{{P_3}}}} \right)\]
We will take the boiling point of water\[{T_L} = 373.125K\], the triple point of water \[{T_R} = 273.16K\], and the pressure difference \[{P_L} - {P_R} = 120torr\]
\[373.125K - 273.16K = (273.16K) \times \dfrac{{120torr}}{{{P_3}}}\]
\[{P_3} = 328torr\]
Now, we will take the triple point of water\[{T_L} = 273.16K\], \[{T_R}\]be the unknown temperature and the pressure difference \[{P_L} - {P_R} = 90torr\]
\[273.16K - {T_R} = \left( {273.16K} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{90torr}}{{328torr}}} \right)\]
\[{T_R} = 348K\]
Hence, the unknown temperature is\[{T_R} = 348K\].
Key point: When one bath is at the triple point and the other is at the boiling point of water, we will take it\[{T_3} = {T_R}\]. When one bath is at the triple point and the other is at an unknown temperature, we will take it\[{T_3} = {T_L}\]. The value of the triple point and boiling point of water is constant.
Note: Manometer could be a device that works on the principle of hydrostatic equilibrium. Hydrostatic equilibrium states that the pressure at any point within a fluid at rest is equal and its value is simply the weight of the overlying liquid. This device is especially used to measure low-pressure differences accurately. Common uses of manometers are flow, filter pressure drop, meter calibrations, leak testing, and tank liquid level.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Let us consider, \[{T_L}\]-Temperature of the left-hand thermometer, and \[{P_L}\]-Pressure in the left-hand thermometer. Similarly, \[{T_R}\]-Temperature of the right-hand thermometer, and \[{P_R}\]-Pressure in the right-hand thermometer.
From the statement given in the problem, the pressure is the same in two thermometers when they are both at the triple point of water. We will take this pressure\[{P_3}\].
\[\dfrac{T}{P} = \dfrac{{{T_3}}}{{{P_3}}} \Rightarrow T = {T_3} \times \dfrac{P}{{{P_3}}}\] \[\left( {\therefore {T_3} = 273.16K} \right)\]-Triple point of water
The equation for both left and both thermometer
\[{T_L} = \left( {273.16K} \right) \times \dfrac{{{P_L}}}{{{P_3}}}\] and \[{T_R} = \left( {273.16K} \right) \times \dfrac{{{P_R}}}{{{P_3}}}\]
Subtract the second equation from the first equation
\[{T_L} - {T_R} = \left( {273.16K} \right) \times \left( {\dfrac{{{P_L} - {P_R}}}{{{P_3}}}} \right)\]
We will take the boiling point of water\[{T_L} = 373.125K\], the triple point of water \[{T_R} = 273.16K\], and the pressure difference \[{P_L} - {P_R} = 120torr\]
\[373.125K - 273.16K = (273.16K) \times \dfrac{{120torr}}{{{P_3}}}\]
\[{P_3} = 328torr\]
Now, we will take the triple point of water\[{T_L} = 273.16K\], \[{T_R}\]be the unknown temperature and the pressure difference \[{P_L} - {P_R} = 90torr\]
\[273.16K - {T_R} = \left( {273.16K} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{90torr}}{{328torr}}} \right)\]
\[{T_R} = 348K\]
Hence, the unknown temperature is\[{T_R} = 348K\].
Key point: When one bath is at the triple point and the other is at the boiling point of water, we will take it\[{T_3} = {T_R}\]. When one bath is at the triple point and the other is at an unknown temperature, we will take it\[{T_3} = {T_L}\]. The value of the triple point and boiling point of water is constant.
Note: Manometer could be a device that works on the principle of hydrostatic equilibrium. Hydrostatic equilibrium states that the pressure at any point within a fluid at rest is equal and its value is simply the weight of the overlying liquid. This device is especially used to measure low-pressure differences accurately. Common uses of manometers are flow, filter pressure drop, meter calibrations, leak testing, and tank liquid level.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




