
A Fischer projection of (2R,3S)-2,3-butanediol is:
(A)
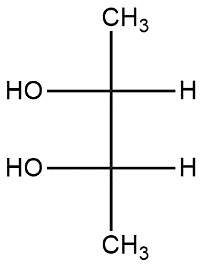
(B)
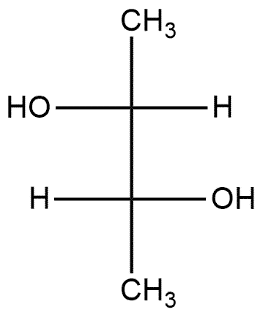
(C)
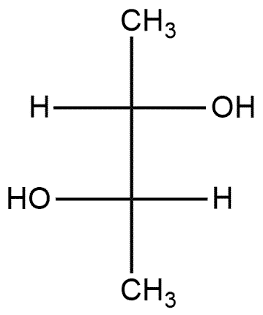
(D)





Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: Fischer projection is a two-dimension (2D) representation of a three-dimension (3D) organic molecule with the help of projection. These are mainly used in biochemistry and organic chemistry to represent monosaccharides.
Complete step by step solution:
Stereoisomers are the isomers having similar bonding patterns but differ in the arrangement of atoms or groups in three-dimensional space. There are two different stereoisomers for a molecule that has a centre of chirality in such cases it is expressed in terms of R and S configuration. For any pair of enantiomers with a chirality centre, one will have R configuration and the other will have the S configuration.
R stands for Rectus which is a Latin word with the meaning right, R is given to the isomer when the sequence is left to right.
S stands for Sinister another Latin word with left, S is given to the isomer if the sequence is right to left.
Also if the sequence follows the clockwise pattern it is known to be R configuration while for anticlockwise it follows S configuration. Priority sequence is decided by the sequence rules also called CIP rules.
In the case of 2,3-butanediol, the preference order according to CIP rules is:
\[OH>C{{H}_{3}}>H\]
Now if we see the option B
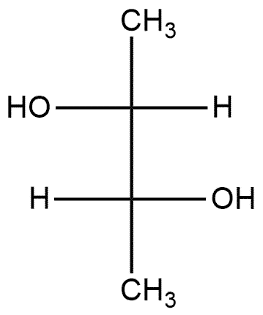
In case of 2nd carbon priority of atoms is started from left to right so it follows R-configuration or on 3rd carbon priority of atoms is started from right to left so it follows S-configuration.
Thus, Fischer projection of (2R,3S)-2,3-butanediol is option (B).
Note: Chiral molecules are those molecules which are not superimposable on their mirror images. Chiral carbon is the carbon which is bonded to different atoms or groups also known by asymmetric carbon.
Complete step by step solution:
Stereoisomers are the isomers having similar bonding patterns but differ in the arrangement of atoms or groups in three-dimensional space. There are two different stereoisomers for a molecule that has a centre of chirality in such cases it is expressed in terms of R and S configuration. For any pair of enantiomers with a chirality centre, one will have R configuration and the other will have the S configuration.
R stands for Rectus which is a Latin word with the meaning right, R is given to the isomer when the sequence is left to right.
S stands for Sinister another Latin word with left, S is given to the isomer if the sequence is right to left.
Also if the sequence follows the clockwise pattern it is known to be R configuration while for anticlockwise it follows S configuration. Priority sequence is decided by the sequence rules also called CIP rules.
In the case of 2,3-butanediol, the preference order according to CIP rules is:
\[OH>C{{H}_{3}}>H\]
Now if we see the option B

In case of 2nd carbon priority of atoms is started from left to right so it follows R-configuration or on 3rd carbon priority of atoms is started from right to left so it follows S-configuration.
Thus, Fischer projection of (2R,3S)-2,3-butanediol is option (B).
Note: Chiral molecules are those molecules which are not superimposable on their mirror images. Chiral carbon is the carbon which is bonded to different atoms or groups also known by asymmetric carbon.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




