
A farmer has a supply of chemical fertilizer of type A which contains 10% nitrogen and 6% phosphoric acid and of type B which contains 5% nitrogen and 10% phosphoric acid. After soil testing, it is found that at least 7 kg of nitrogen and the same quantity of phosphoric acid is required for a good crop. The fertilizer of type A costs Rs. 5 per kg and the type B costs 8 per kg. Using linear programming, find how many kilograms of each type of the fertilizer should be brought to meet the requirement and for the cost to be minimum. Find the feasible region in the graph.
Answer
608.1k+ views
Hint: Find the equation to minimize nitrogen and phosphoric acid of type A and type B. Find the required equations and plot them in the graph, where \[x\ge 0\] and \[y\ge 0\]. Find the intersection point of the line and substitute it in the equation of minimization to get the cost.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let the farmer use x kg of fertilizer of type A and y kg of type B.
The type A contains 10% nitrogen and 6% phosphoric acid.
Similarly, type B contains 5% nitrogen and 10% phosphoric acid.
The type A fertilizer costs Rs. 5 per kg. and type B fertilizer costs rupees 8 per kg.
Thus we can minimize Z as,
minimize \[z=5x+8y\]
which is multiplied by the kg of the fertilizer.
After soil tests they concluded that at least 7 kg of nitrogen and phosphoric acid is required for a good crop.
Thus, 10% of nitrogen is for type A and 5% of nitrogen is for type B.
\[10%x+5%y\ge 7\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{10}{100}x+\dfrac{5}{100}y\ge 7\] [Cross multiply and simplify]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 10x+5y\ge 7\times 100 \\
& 10x+5y\ge 40.........(1) \\
\end{align}\]
Similarly 6% of phosphoric acid for type A and 10% for type B
\[\therefore 6%x+10%y\ge 7\]
\[\dfrac{6}{100}x+\dfrac{10}{100}y\ge 7\] [Cross multiply and simplify]
\[\begin{align}
& 6x+10y\ge 700 \\
& \therefore 3x+5y\ge 350.........(2) \\
\end{align}\]
We got 2 equations,
\[2x+y\ge 140\] and \[3x+5y\ge 350\]
\[x\ge 0\] and \[y\ge 0\]
Consider \[2x+y=140.\] The table of solution is,
Thus we got points (70, 0) and (0, 140)
Consider \[3x+5y=350\]. The table of the solution is,
Thus we get the points (0, 70) and (115, 1).
Now let us plot these equations in the graph.
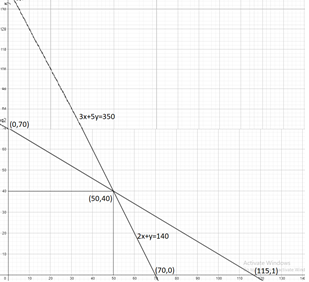
Thus we got the point of their intersection as (50, 40).
We can evaluate the value z using the corner points from the graph (0, 140), (50, 40), (115, 1).
Let us draw a table to make it easier to calculate.
Thus we got the minimum value of x as 570.
Since the feasible region is unbounded, thus we got the inequality does not have any common points except (50, 40) so the minimum value of Z = Rs. 570 at (50, 40).
Thus the farmer must buy 50 kg of chemical of type A and 40 kg of chemical of type B.
Note: The limitations that we may face here are that it might not be easy to define a specific objective function. They have only a single objective, i.e. profit maximization or cost maximization. In linear programming we assume that the values of coefficient of decision variables are known with certainty.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let the farmer use x kg of fertilizer of type A and y kg of type B.
The type A contains 10% nitrogen and 6% phosphoric acid.
Similarly, type B contains 5% nitrogen and 10% phosphoric acid.
The type A fertilizer costs Rs. 5 per kg. and type B fertilizer costs rupees 8 per kg.
Thus we can minimize Z as,
minimize \[z=5x+8y\]
which is multiplied by the kg of the fertilizer.
After soil tests they concluded that at least 7 kg of nitrogen and phosphoric acid is required for a good crop.
Thus, 10% of nitrogen is for type A and 5% of nitrogen is for type B.
\[10%x+5%y\ge 7\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{10}{100}x+\dfrac{5}{100}y\ge 7\] [Cross multiply and simplify]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 10x+5y\ge 7\times 100 \\
& 10x+5y\ge 40.........(1) \\
\end{align}\]
Similarly 6% of phosphoric acid for type A and 10% for type B
\[\therefore 6%x+10%y\ge 7\]
\[\dfrac{6}{100}x+\dfrac{10}{100}y\ge 7\] [Cross multiply and simplify]
\[\begin{align}
& 6x+10y\ge 700 \\
& \therefore 3x+5y\ge 350.........(2) \\
\end{align}\]
We got 2 equations,
\[2x+y\ge 140\] and \[3x+5y\ge 350\]
\[x\ge 0\] and \[y\ge 0\]
Consider \[2x+y=140.\] The table of solution is,
| X | 70 | 0 |
| y | 0 | 140 |
Thus we got points (70, 0) and (0, 140)
Consider \[3x+5y=350\]. The table of the solution is,
| X | 0 | 115 |
| y | 70 | 1 |
Thus we get the points (0, 70) and (115, 1).
Now let us plot these equations in the graph.

Thus we got the point of their intersection as (50, 40).
We can evaluate the value z using the corner points from the graph (0, 140), (50, 40), (115, 1).
Let us draw a table to make it easier to calculate.
| Corner Point | Z=5x+8y |
| (115, 1) | \[\begin{align} & Z=5\times 115+8\times 1 \\ & =583 \\ \end{align}\] |
| (50, 40) | \[\begin{align} & Z=5\times 115+8\times 40 \\ & =250+320=570 \\ & (Minimum) \\ \end{align}\] |
| (0, 140) | \[\begin{align} & Z=5\times 0+8\times 140 \\ & =1120 \\ \end{align}\] |
Thus we got the minimum value of x as 570.
Since the feasible region is unbounded, thus we got the inequality does not have any common points except (50, 40) so the minimum value of Z = Rs. 570 at (50, 40).
Thus the farmer must buy 50 kg of chemical of type A and 40 kg of chemical of type B.
Note: The limitations that we may face here are that it might not be easy to define a specific objective function. They have only a single objective, i.e. profit maximization or cost maximization. In linear programming we assume that the values of coefficient of decision variables are known with certainty.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




