
a) Explain Schottky defect and Frenkel defect
b) Write briefly the adsorption theory of catalysis.
Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint:Point defects are the irregularities from the ideal arrangement around a point or atom in a crystalline substance. Points defect are of three types. These are Stoichiometric defect, impurity defect and non- stoichiometric defects. Catalysts are the substance which affects the rate of the reaction by providing the reaction a different pathway.
Complete answer:
A) Crystals are not perfect. Solid consists of an aggregate of a large number of small crystals. These small crystals have defects in them. Ionic solids must always maintain electrical neutrality. So rather than vacancy or interstitial defects the ionic solid shows Schottky defects and Frenkel defects.
Schottky defect is basically a vacancy defect; it arises when equal numbers of cations and anions are missing from the lattice structure. It is very common in the ionic compounds having high coordination numbers; both anion and cation are of equal size. For example - potassium bromide, sodium chloride etc. Schottky defects also decrease the density of the solid.
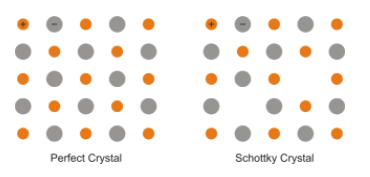
Frenkel defects are also known as dislocation effects, occur in ionic solid in which the smaller ion is dislocated from its site to the interstitial site and produce vacancy defect in the original site and interstitial defect at the new site. It does not change the density of the solid. Generally occur in ionic solid having a difference between the size of cation and anion. For example- zinc sulphide, silver chloride etc.
B) A catalyst influences the rate of reaction by providing the reaction a different pathway. In Adsorption theory of catalysis, the reactants in their gaseous state or in dissolved state in solution get adsorbed on the surface of the catalyst in its solid state.
There are free valencies on the surface of the solid catalyst. First the diffusion of reactant molecules occurs in the surface of the catalyst. Then the adsorption of reactants occurs by forming loose bonds with the catalysts because of those free valencies. Then the chemical reaction takes place between the reactants. After the reaction has completed, desorption occurs and products get released from the surface of the catalyst.
Note:Catalysts are of two types depending upon the phases of catalyst and reactants. Homogeneous catalyst is a catalyst in which the reactant and catalyst are present in the same phase. Heterogeneous catalyst in which both reactant and catalyst are in different phase
Complete answer:
A) Crystals are not perfect. Solid consists of an aggregate of a large number of small crystals. These small crystals have defects in them. Ionic solids must always maintain electrical neutrality. So rather than vacancy or interstitial defects the ionic solid shows Schottky defects and Frenkel defects.
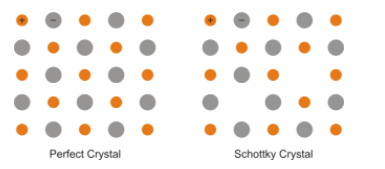
Schottky defect is basically a vacancy defect; it arises when equal numbers of cations and anions are missing from the lattice structure. It is very common in the ionic compounds having high coordination numbers; both anion and cation are of equal size. For example - potassium bromide, sodium chloride etc. Schottky defects also decrease the density of the solid.

Frenkel defects are also known as dislocation effects, occur in ionic solid in which the smaller ion is dislocated from its site to the interstitial site and produce vacancy defect in the original site and interstitial defect at the new site. It does not change the density of the solid. Generally occur in ionic solid having a difference between the size of cation and anion. For example- zinc sulphide, silver chloride etc.

B) A catalyst influences the rate of reaction by providing the reaction a different pathway. In Adsorption theory of catalysis, the reactants in their gaseous state or in dissolved state in solution get adsorbed on the surface of the catalyst in its solid state.
There are free valencies on the surface of the solid catalyst. First the diffusion of reactant molecules occurs in the surface of the catalyst. Then the adsorption of reactants occurs by forming loose bonds with the catalysts because of those free valencies. Then the chemical reaction takes place between the reactants. After the reaction has completed, desorption occurs and products get released from the surface of the catalyst.
Note:Catalysts are of two types depending upon the phases of catalyst and reactants. Homogeneous catalyst is a catalyst in which the reactant and catalyst are present in the same phase. Heterogeneous catalyst in which both reactant and catalyst are in different phase
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




