
(a) Draw the labelled diagram of Daniel cell.
(b) Write the half-reactions of oxidation and reduction taking place on electrodes.
Answer
520.5k+ views
Hint: Recollect the difference between an electrolytic cell and galvanic cell. Where does oxidation take place in a galvanic cell? Think about the direction of electron flow in a galvanic cell.
Complete answer:
Galvanic cell is an electrochemical cell which converts chemical energy to electrical energy. Some examples include dry cell, fuel cell, Ni-Cd battery, lead storage cell.
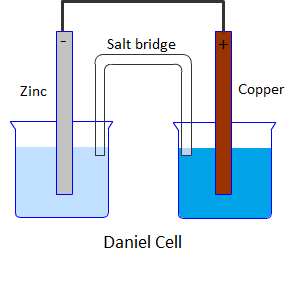
Daniel cell is a galvanic cell in which a spontaneous chemical reaction takes place to produce electricity. It consists of two half cells. One half cell is a beaker containing a strip of metallic zinc dipped in 1M aqueous zinc sulphate solution. The second half cell consists of a beaker having a metallic strip of copper immersed in 1M aqueous copper sulphate solution. The two solutions are connected with the help of a salt bridge containing saturated solution of KCl in agar agar gel.
Daniel cell can be schematically represented as,
\[\left. Zn \right|\left. ZnS{{O}_{4}}(0.1M) \right\|\left. CuS{{O}_{4}}(0.1M) \right|Cu\]
Diagrammatically Daniel cell can be represented as:
Half-cell reactions:
-At Anode (Oxidation half-cell):
\[Zn(s)\to Z{{n}^{2+}}+2{{e}^{-}}\]
-At Cathode (Reduction half-cell):
\[C{{u}^{2+}}+2{{e}^{-}}\to Cu(s)\]
Note: Don’t get confused with charge on anode and cathode in electrolytic cell and galvanic cell. Remember LOAN-Left Oxidation Anode. In electrolytic cells, positively electrode is anode and negatively charged electrode is cathode. In galvanic cells, it is opposite. Positively charged electrode is a cathode and a negatively charged electrode is anode.
Complete answer:
Galvanic cell is an electrochemical cell which converts chemical energy to electrical energy. Some examples include dry cell, fuel cell, Ni-Cd battery, lead storage cell.
Daniel cell is a galvanic cell in which a spontaneous chemical reaction takes place to produce electricity. It consists of two half cells. One half cell is a beaker containing a strip of metallic zinc dipped in 1M aqueous zinc sulphate solution. The second half cell consists of a beaker having a metallic strip of copper immersed in 1M aqueous copper sulphate solution. The two solutions are connected with the help of a salt bridge containing saturated solution of KCl in agar agar gel.
Daniel cell can be schematically represented as,
\[\left. Zn \right|\left. ZnS{{O}_{4}}(0.1M) \right\|\left. CuS{{O}_{4}}(0.1M) \right|Cu\]
Diagrammatically Daniel cell can be represented as:

Half-cell reactions:
-At Anode (Oxidation half-cell):
\[Zn(s)\to Z{{n}^{2+}}+2{{e}^{-}}\]
-At Cathode (Reduction half-cell):
\[C{{u}^{2+}}+2{{e}^{-}}\to Cu(s)\]
Note: Don’t get confused with charge on anode and cathode in electrolytic cell and galvanic cell. Remember LOAN-Left Oxidation Anode. In electrolytic cells, positively electrode is anode and negatively charged electrode is cathode. In galvanic cells, it is opposite. Positively charged electrode is a cathode and a negatively charged electrode is anode.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




