
(a) Draw a ray diagram to represent a convex mirror. On this diagram mark the principal axis, principal focus F and the centre of curvature C if the focal length of the convex mirror is \[3\,cm\].
(b) An object \[1\,cm\] tall is placed \[30\,cm\] in front of a convex mirror of focal length \[20\,cm\]. Find the size and position of the image formed by the convex mirror.
Answer
524.1k+ views
Hint:Study about mirrors and learn about different parts of a mirror. Use the mirror's formula to find the position and property of the image. Principal axis of a mirror is the line joining the centre of curvature, principal focus and midpoint of any mirror.
Formula used:
Mirror’s formula is given by, \[\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}\]
where, \[v\]is the image distance, \[u\] is the object distance and \[f\] is the focal length of the mirror.
Magnification in a mirror is given by, \[m = \dfrac{{{h_i}}}{{{h_o}}} = \dfrac{v}{u}\]
where, \[m\] is the magnification of the object, \[{h_i}\] is the image height and \[{h_o}\] is the object height.
Complete step by step answer:
(a) The marked diagram of a convex mirror with focal length \[3cm\] is given below.
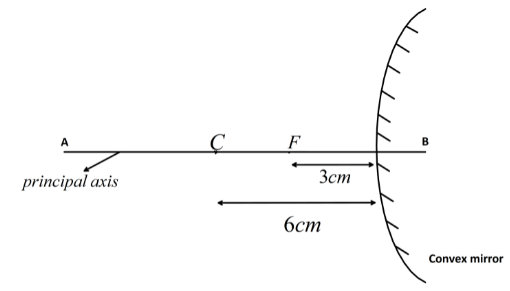
In the figure, AB is the principal axis, F is the principal focus and C is the centre of curvature.
(b) Here we have given an object of length \[{h_o} = 1\,cm\] and distance of the object from the mirror is, \[u = - 30\,cm\] focal length of the given convex mirror is \[f = - 20\,cm\] (Since, it is a mirror). Now, from mirror’s formula we have, \[\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}\] where, \[v\] is the image distance, \[u\] is the object distance and \[f\] is the focal length of the mirror.
So, putting the values of object distance \[u = - 30\,cm\] and focal length of the mirror \[f = - 20\,cm\] we have,
\[\dfrac{1}{{ - 30}} + \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{{ - 20}}\]
\[\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{{30}} - \dfrac{1}{{20}}\]
Simplifying we have,
\[\dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{{2 - 3}}{{60}}\]
\[\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{{60}}\]
\[\Rightarrow v = - 60\,cm\]
Now, we know magnification in a mirror is given by, \[m = \dfrac{{{h_i}}}{{{h_o}}} = \dfrac{v}{u}\] where, \[{h_i}\] is the image height and \[{h_o}\] is the object height.
So, putting, object height \[{h_o} = 1\,cm\] object distance \[u = - 30\,cm\] and image distance \[v = - 60\,cm\] we have,
\[\dfrac{{{h_i}}}{1} = \dfrac{{ - 60}}{{ - 30}}\]
\[\therefore {h_i} = 2\,cm\].
Hence, the image will be at a distance of \[60\,cm\] in front of the mirror and the image will be erect, real and magnified twice.
Note: The negative sign implies that the distance is in the left of the mirror. The distance measured to the left of the incident ray is taken to be negative and the distance measured to the right of the incident ray is taken to be always positive. If the image is formed behind the mirror the image will be said to be a virtual image.
Formula used:
Mirror’s formula is given by, \[\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}\]
where, \[v\]is the image distance, \[u\] is the object distance and \[f\] is the focal length of the mirror.
Magnification in a mirror is given by, \[m = \dfrac{{{h_i}}}{{{h_o}}} = \dfrac{v}{u}\]
where, \[m\] is the magnification of the object, \[{h_i}\] is the image height and \[{h_o}\] is the object height.
Complete step by step answer:
(a) The marked diagram of a convex mirror with focal length \[3cm\] is given below.

In the figure, AB is the principal axis, F is the principal focus and C is the centre of curvature.
(b) Here we have given an object of length \[{h_o} = 1\,cm\] and distance of the object from the mirror is, \[u = - 30\,cm\] focal length of the given convex mirror is \[f = - 20\,cm\] (Since, it is a mirror). Now, from mirror’s formula we have, \[\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}\] where, \[v\] is the image distance, \[u\] is the object distance and \[f\] is the focal length of the mirror.
So, putting the values of object distance \[u = - 30\,cm\] and focal length of the mirror \[f = - 20\,cm\] we have,
\[\dfrac{1}{{ - 30}} + \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{{ - 20}}\]
\[\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{{30}} - \dfrac{1}{{20}}\]
Simplifying we have,
\[\dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{{2 - 3}}{{60}}\]
\[\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{{60}}\]
\[\Rightarrow v = - 60\,cm\]
Now, we know magnification in a mirror is given by, \[m = \dfrac{{{h_i}}}{{{h_o}}} = \dfrac{v}{u}\] where, \[{h_i}\] is the image height and \[{h_o}\] is the object height.
So, putting, object height \[{h_o} = 1\,cm\] object distance \[u = - 30\,cm\] and image distance \[v = - 60\,cm\] we have,
\[\dfrac{{{h_i}}}{1} = \dfrac{{ - 60}}{{ - 30}}\]
\[\therefore {h_i} = 2\,cm\].
Hence, the image will be at a distance of \[60\,cm\] in front of the mirror and the image will be erect, real and magnified twice.
Note: The negative sign implies that the distance is in the left of the mirror. The distance measured to the left of the incident ray is taken to be negative and the distance measured to the right of the incident ray is taken to be always positive. If the image is formed behind the mirror the image will be said to be a virtual image.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




