
A dipole is said to be in stable equilibrium when angle between electric field and dipole moment is
A). Zero
B). 180 degree
C). 45 degree
D). 90 degree
Answer
530.1k+ views
Hint: In this question, the dipole is kept in a uniform electric field. And we have to write the expressions for them in two different cases. So for solving this, we will keep the dipole at two positions and then, will find the dipole at \[\theta = {0^ \circ }\] and at \[\theta = {180^ \circ }\].
Formula used:
The potential energy of the dipole will be equal to the
\[U = - P{E_0}\cos \theta \]
And for torque, the formula will be
\[\tau = P{E_0}\sin \theta \]
Here,
\[U\], will be the potential energy of the dipole
\[\tau \], will be the torque
\[P\], will be the electric dipole of the dipole moment
\[{E_0}\], will be the uniform electric field
Complete step-by-step solution:
Let us assume that the dipole we are using is kept at two positions namely (a) and (b) which is placed in a constant electric field \[{E_0}\] as it is shown in the below diagram.
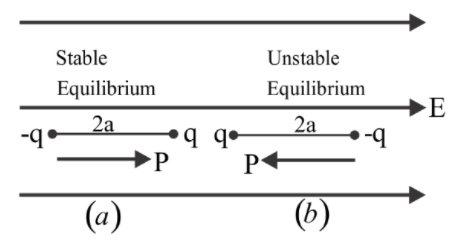
In the first case: When the angle between the dipole and electric field will be zero
Then, the Potential energy of the dipole will be equal to the
\[U = - P{E_0}\cos \theta \]
Therefore,
\[U = - P{E_0}\cos {0^ \circ }\]
And on simplifying the equation, we get
since \[\cos {0^ \circ } = 1\]
\[U = - P{E_0}\]
Therefore, we can say that the dipole will be in stable equilibrium.
Now we will find the torque,
And for torque, the formula will be
\[ \tau = P{E_0}\sin \theta \]
\[\Rightarrow \tau = P{E_0}\sin {0^ \circ } \]
\[\Rightarrow \tau = 0 \]
Hence, the option A is correct.
In the second case: When the angle between the dipole and electric field will be ${180}^{\circ}$
Then, the Potential energy of the dipole will be equal to the
\[ U = - P{E_0}\cos \theta \]
\[\Rightarrow U = - P{E_0}\cos {180^ \circ } \]
\[\Rightarrow U = P{E_0} \] \[\left( {\therefore \cos {{180}^ \circ } = - 1} \right)\]
Therefore, we can say that the dipole will be in unstable equilibrium.
Now we will find the torque,
And for torque, the formula will be
\[ \tau = P{E_0}\sin \theta \]
\[\Rightarrow \tau = P{E_0}\sin {180^ \circ } \]
\[\Rightarrow \tau = 0 \]
Note: Stable equilibrium means the lowest potential energy at the equilibrium point. Therefore the stable equilibrium the torque should be zero and the potential energy of the dipole should be minimum. Whereas the unstable equilibrium torque will be zero and the potential energy should be maximum or positive.
Formula used:
The potential energy of the dipole will be equal to the
\[U = - P{E_0}\cos \theta \]
And for torque, the formula will be
\[\tau = P{E_0}\sin \theta \]
Here,
\[U\], will be the potential energy of the dipole
\[\tau \], will be the torque
\[P\], will be the electric dipole of the dipole moment
\[{E_0}\], will be the uniform electric field
Complete step-by-step solution:
Let us assume that the dipole we are using is kept at two positions namely (a) and (b) which is placed in a constant electric field \[{E_0}\] as it is shown in the below diagram.

In the first case: When the angle between the dipole and electric field will be zero
Then, the Potential energy of the dipole will be equal to the
\[U = - P{E_0}\cos \theta \]
Therefore,
\[U = - P{E_0}\cos {0^ \circ }\]
And on simplifying the equation, we get
since \[\cos {0^ \circ } = 1\]
\[U = - P{E_0}\]
Therefore, we can say that the dipole will be in stable equilibrium.
Now we will find the torque,
And for torque, the formula will be
\[ \tau = P{E_0}\sin \theta \]
\[\Rightarrow \tau = P{E_0}\sin {0^ \circ } \]
\[\Rightarrow \tau = 0 \]
Hence, the option A is correct.
In the second case: When the angle between the dipole and electric field will be ${180}^{\circ}$
Then, the Potential energy of the dipole will be equal to the
\[ U = - P{E_0}\cos \theta \]
\[\Rightarrow U = - P{E_0}\cos {180^ \circ } \]
\[\Rightarrow U = P{E_0} \] \[\left( {\therefore \cos {{180}^ \circ } = - 1} \right)\]
Therefore, we can say that the dipole will be in unstable equilibrium.
Now we will find the torque,
And for torque, the formula will be
\[ \tau = P{E_0}\sin \theta \]
\[\Rightarrow \tau = P{E_0}\sin {180^ \circ } \]
\[\Rightarrow \tau = 0 \]
Note: Stable equilibrium means the lowest potential energy at the equilibrium point. Therefore the stable equilibrium the torque should be zero and the potential energy of the dipole should be minimum. Whereas the unstable equilibrium torque will be zero and the potential energy should be maximum or positive.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




