
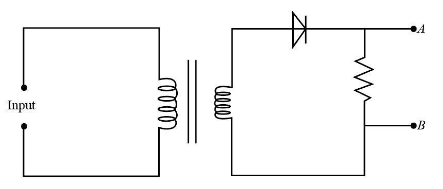
A diode is connected to the output of a transformer as shown in the figure given below. Analyse the figure
(a) Draw a time-voltage graph for the current obtained across AB.
(b) What is the function of the diode in the circuit?

Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint:The circuit given in the question is the half-wave rectifier, in which only one crystal is present in the circuit. At the input, when we give AC supply, only the positive half cycle appears on the load, and the negative half cycles get removed or suppressed. The diode that we use is the PN junction diode. We can say that because of the diode, the current will flow in only one direction. As a result of that, AC voltage changes to DC voltage.
Complete step by step answer:
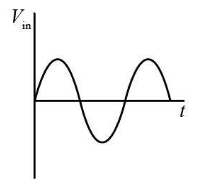
(a) When we give AC supply at the input, the voltage in the secondary winding can be represented as:
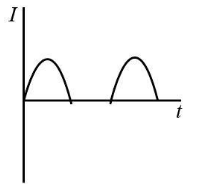
Now, for the positive half cycle, the crystal diode will behave as forward biased. It will lead to conduction through diodes and the current will flow through the resistors. The current flow can be represented as:
Hence, for the positive half cycle, we can represent output voltage as:
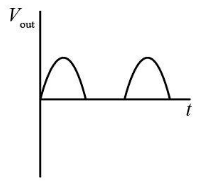
Hence We can draw the voltage time graph as represented below:
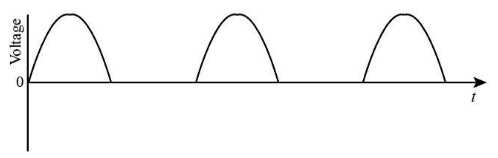
(b) As explained above, for the positive half cycle, the crystal diode will behave as forward biased. It will lead to conduction through the diode, and the current will flow through the resistors. But for the negative half cycle, the diode will behave as reversed biased, and hence maximum voltage in the diode will be termed as peak inverse voltage. As a result of this, current flows through the resistor, but the output obtained is pulsating in nature. Hence we can say that the diode in the circuit works as a rectifier. The diode will only allow cycles with positive voltage but will block the negative voltage cycle. The diode works as a rectifier in the circuit. It allows only the positive voltage cycle to flow through the circuit and blocks the negative cycle.
Note:The transformer provides the AC supply, which is to be rectified. The key role of the transformer to step up and step up the supply voltage according to the requirements. The transformer also helps in the isolation of rectifiers from the power supply lines, which can reduce the risk of shock. In the half-wave rectifier a crystal diode is used, but for the full-wave rectifier, two crystal diodes are used.
Complete step by step answer:
(a) When we give AC supply at the input, the voltage in the secondary winding can be represented as:

Now, for the positive half cycle, the crystal diode will behave as forward biased. It will lead to conduction through diodes and the current will flow through the resistors. The current flow can be represented as:

Hence, for the positive half cycle, we can represent output voltage as:

Hence We can draw the voltage time graph as represented below:

(b) As explained above, for the positive half cycle, the crystal diode will behave as forward biased. It will lead to conduction through the diode, and the current will flow through the resistors. But for the negative half cycle, the diode will behave as reversed biased, and hence maximum voltage in the diode will be termed as peak inverse voltage. As a result of this, current flows through the resistor, but the output obtained is pulsating in nature. Hence we can say that the diode in the circuit works as a rectifier. The diode will only allow cycles with positive voltage but will block the negative voltage cycle. The diode works as a rectifier in the circuit. It allows only the positive voltage cycle to flow through the circuit and blocks the negative cycle.
Note:The transformer provides the AC supply, which is to be rectified. The key role of the transformer to step up and step up the supply voltage according to the requirements. The transformer also helps in the isolation of rectifiers from the power supply lines, which can reduce the risk of shock. In the half-wave rectifier a crystal diode is used, but for the full-wave rectifier, two crystal diodes are used.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




