
A cubical block of side 7cm is surmounted by hemisphere. What is the greatest diameter the hemisphere can have? Find the total surface area (TSA) of the solid.
Answer
624.6k+ views
- Hint: to solve this question we will use some formulae which are given as, the formula for TSA of a cube of side a is given by \[6{{a}^{2}}\], the formula for the base of the hemisphere is given by the area of circle of radius r, which is \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\], and the formula for CSA of hemisphere is given by \[2\pi {{r}^{2}}\], where r is the radius of the hemisphere.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Given that the cubical block of side 7cm is surmounted by hemisphere.
We have to find the greatest diameter the hemisphere can have. And the total surface area of the solid.
The figure which illustrates the given situation of the question is given as below.
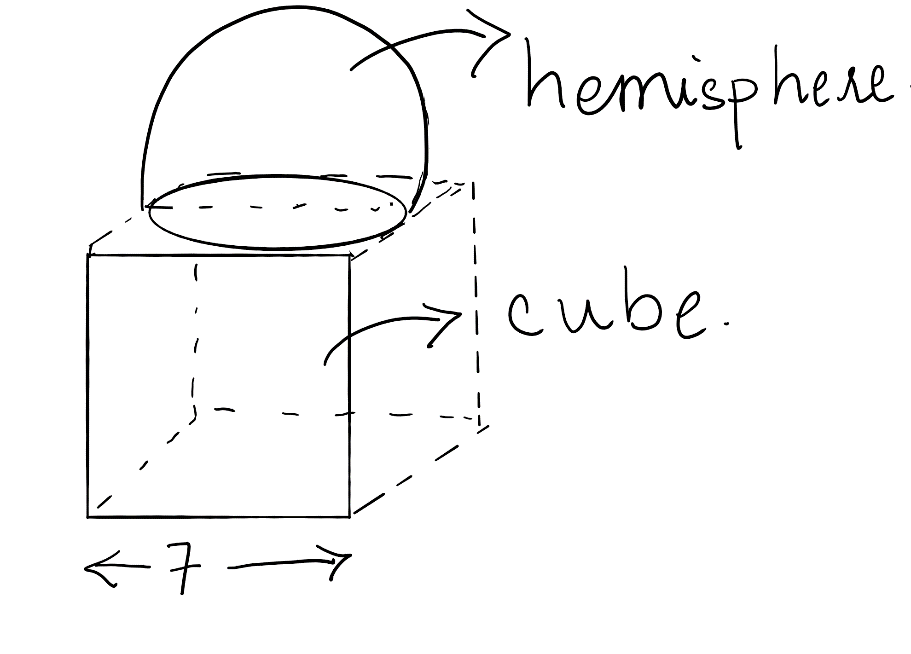
Therefore, we see as the hemisphere is mounted on the cubical block. So, observing the figure we get that the diameter of the hemisphere is equal to the side of the cube, which is 7cm.
So, we get that the diameter of the hemisphere is 7cm.
Then the radius r would be \[\dfrac{7}{2}=3.5cm\].
Now we have to determine the total surface area of the generated solid.
Observing the figure, we see that the base of the hemisphere is covered inside one side of the cube. Therefore, we need to subtract the area of base of the hemisphere.
So, the TSA of the solid = TSA of cube - Area of base of hemisphere + CSA of hemisphere……(i)
The formula for TSA of a cube of side a is given by \[6{{a}^{2}}\].
The formula for the base of the hemisphere is given by the area of the circle of radius r, which is \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\].
Again, the formula for CSA of the hemisphere is given by \[2\pi {{r}^{2}}\], where r is the radius of the hemisphere.
Substituting the above stated formulae in equation (i) and substituting the value of side of the cube as a = 7cm and the radius of the hemisphere as r = 3.5cm, we get the TSA of generated solid as,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow TSA=6\times 7{}^\text{2}-~\pi \times \left( 3.5 \right){}^\text{2}+\text{ }2\times \pi \times \left( 3.5 \right){}^\text{2} \\
& \Rightarrow TSA=6\times 7{}^\text{2}+\pi \times \left( 3.5 \right){}^\text{2} \\
& \Rightarrow TSA\text{ }=\text{ }332.\text{ }465\text{ }cm{}^\text{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, we got the Total surface area (TSA) of the generated solid is \[332.\text{ }465\text{ }cm{}^\text{2}\].
Note: The possibility of error in these types of questions can be at the point where you have to calculate the TSA of the generated solid. Always keep in mind that because the base of the hemisphere is covered inside one side of the cube, therefore we need to subtract the area of the base of the hemisphere to obtain the result.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Given that the cubical block of side 7cm is surmounted by hemisphere.
We have to find the greatest diameter the hemisphere can have. And the total surface area of the solid.
The figure which illustrates the given situation of the question is given as below.

Therefore, we see as the hemisphere is mounted on the cubical block. So, observing the figure we get that the diameter of the hemisphere is equal to the side of the cube, which is 7cm.
So, we get that the diameter of the hemisphere is 7cm.
Then the radius r would be \[\dfrac{7}{2}=3.5cm\].
Now we have to determine the total surface area of the generated solid.
Observing the figure, we see that the base of the hemisphere is covered inside one side of the cube. Therefore, we need to subtract the area of base of the hemisphere.
So, the TSA of the solid = TSA of cube - Area of base of hemisphere + CSA of hemisphere……(i)
The formula for TSA of a cube of side a is given by \[6{{a}^{2}}\].
The formula for the base of the hemisphere is given by the area of the circle of radius r, which is \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\].
Again, the formula for CSA of the hemisphere is given by \[2\pi {{r}^{2}}\], where r is the radius of the hemisphere.
Substituting the above stated formulae in equation (i) and substituting the value of side of the cube as a = 7cm and the radius of the hemisphere as r = 3.5cm, we get the TSA of generated solid as,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow TSA=6\times 7{}^\text{2}-~\pi \times \left( 3.5 \right){}^\text{2}+\text{ }2\times \pi \times \left( 3.5 \right){}^\text{2} \\
& \Rightarrow TSA=6\times 7{}^\text{2}+\pi \times \left( 3.5 \right){}^\text{2} \\
& \Rightarrow TSA\text{ }=\text{ }332.\text{ }465\text{ }cm{}^\text{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, we got the Total surface area (TSA) of the generated solid is \[332.\text{ }465\text{ }cm{}^\text{2}\].
Note: The possibility of error in these types of questions can be at the point where you have to calculate the TSA of the generated solid. Always keep in mind that because the base of the hemisphere is covered inside one side of the cube, therefore we need to subtract the area of the base of the hemisphere to obtain the result.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Who is known as the "Little Master" in Indian cricket history?

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

Which are the three major ports of Tamil Nadu A Chennai class 10 social science CBSE

The highest dam in India is A Bhakra dam B Tehri dam class 10 social science CBSE

Describe the process of Unification of Italy class 10 social science CBSE




