
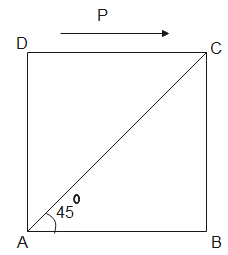
A cube of side $a$ is subjected to shear stress P as shown in the figure. Determine tangential and normal stress along diagonal AC.

Answer
556.2k+ views
Hint: Stress acting on a body is the force applied per unit area. It causes the shape, area or volume of a body. A shearing force is being applied on the cube; this means that it will change the shape of the cube along its diagonal. The shearing stress is parallel to the area.
Formulas used:
$\tau =\dfrac{F}{A}$
Complete answer:
When a force is applied on a body such that the body gets deformed by slipping between planes, such a force applied per unit area is called the shearing or tangential stress. Its SI unit is $N{{m}^{-2}}$. It is given by-
$\tau =\dfrac{F}{A}$ - (1)
Here, $\tau $ is the shearing stress
$F$ is the force applied parallel to its side
$A$ is the displaced area
When a tangential stress, $P$ is applied on cube of side a, it changes its shape as sown in the figure below
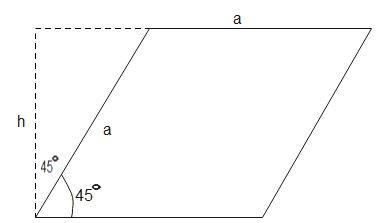
From the above figure,
$\begin{align}
& h=a\cos {{45}^{o}} \\
& \Rightarrow h=\dfrac{a}{\sqrt{2}} \\
\end{align}$
The area of the deformed figure will be-
$\begin{align}
& A=b\times h \\
& \Rightarrow A=a\times \dfrac{a}{\sqrt{2}} \\
& \therefore A=\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}}{\sqrt{2}} \\
\end{align}$
The area of the figure is $\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}}{\sqrt{2}}$ sq units.
From eq (1), the shearing stress acting on the cube will be-
$\begin{align}
& \tau =\dfrac{P}{\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}}{\sqrt{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \tau =\dfrac{\sqrt{2}P}{{{a}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the shearing or tangential stress acting on the cube is $\dfrac{\sqrt{2}P}{{{a}^{2}}}$.
As there is no tension or compression acting on the cube, the normal stress acting on it is zero.
Therefore, the tangential stress on the cube is $\dfrac{\sqrt{2}P}{{{a}^{2}}}$ and the normal stress is zero.
Note:
Normal stress occurs when a body is kept under compression or tension due to which its dimensions change. The force applied in a shearing stress is parallel to the cross sectional area. After stress is applied, a restoring force is developed in the body which tends to bring it back to its original shape.
Formulas used:
$\tau =\dfrac{F}{A}$
Complete answer:
When a force is applied on a body such that the body gets deformed by slipping between planes, such a force applied per unit area is called the shearing or tangential stress. Its SI unit is $N{{m}^{-2}}$. It is given by-
$\tau =\dfrac{F}{A}$ - (1)
Here, $\tau $ is the shearing stress
$F$ is the force applied parallel to its side
$A$ is the displaced area
When a tangential stress, $P$ is applied on cube of side a, it changes its shape as sown in the figure below

From the above figure,
$\begin{align}
& h=a\cos {{45}^{o}} \\
& \Rightarrow h=\dfrac{a}{\sqrt{2}} \\
\end{align}$
The area of the deformed figure will be-
$\begin{align}
& A=b\times h \\
& \Rightarrow A=a\times \dfrac{a}{\sqrt{2}} \\
& \therefore A=\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}}{\sqrt{2}} \\
\end{align}$
The area of the figure is $\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}}{\sqrt{2}}$ sq units.
From eq (1), the shearing stress acting on the cube will be-
$\begin{align}
& \tau =\dfrac{P}{\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}}{\sqrt{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \tau =\dfrac{\sqrt{2}P}{{{a}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the shearing or tangential stress acting on the cube is $\dfrac{\sqrt{2}P}{{{a}^{2}}}$.
As there is no tension or compression acting on the cube, the normal stress acting on it is zero.
Therefore, the tangential stress on the cube is $\dfrac{\sqrt{2}P}{{{a}^{2}}}$ and the normal stress is zero.
Note:
Normal stress occurs when a body is kept under compression or tension due to which its dimensions change. The force applied in a shearing stress is parallel to the cross sectional area. After stress is applied, a restoring force is developed in the body which tends to bring it back to its original shape.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




