
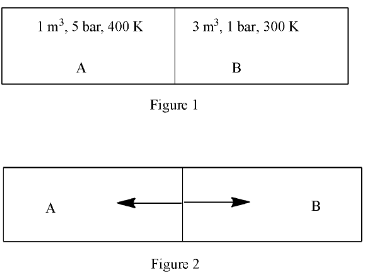
A closed tank has two compartments A and B, both filled with oxygen (assumed to be an ideal gas). The partition separating the two compartments is fixed and is a perfect heat insulator (Figure 1). If the old partition is replaced by a new partition, which can slide and conduct heat does not allow the gas to leak across (Figure 2), the volume (in ${{m}^{3}}$) of the compartment A after the system attains equilibrium is ______________

Answer
538.2k+ views
Hint: We can solve this question by using many formulas like $n=\dfrac{PV}{TR}$, $\dfrac{{{P}_{A}}}{{{T}_{A}}}=\dfrac{{{P}_{B}}}{{{T}_{B}}}$, where P is the pressure, V is the volume, R is the gas constant, T is the temperature, n is the number of moles.
Complete step-by-step answer: So according to Figure 1, in compartment A, the pressure is 5 bar, the volume is 1 ${{m}^{3}}$, and temperature 400 K. This can be written as:
${{P}_{A}}=5$
${{V}_{A}}=1$
${{T}_{1}}=400$
In compartment B, the pressure is 1 bar, the volume is 3 ${{m}^{3}}$, and temperature 400 K. This can be written as:
${{P}_{B}}=1$
${{V}_{B}}=3$
${{T}_{B}}=300$
So, from the given values we can calculate the number of moles for both the compartments by using the formula $n=\dfrac{PV}{TR}$, we get
${{n}_{A}}=\dfrac{\text{ 5 x 1}}{400\text{ x R}}=\dfrac{5}{400R}$
${{n}_{B}}=\dfrac{\text{ 1 x 3}}{300\text{ x R}}=\dfrac{3}{300R}$
The total volume will be = 1 + 3 = 4 ${{m}^{3}}$
In Figure 2, let us assume, the volume of A is x and volume of B is (4 – x).
We know that:
$\dfrac{{{P}_{A}}}{{{T}_{A}}}=\dfrac{{{P}_{B}}}{{{T}_{B}}}$, because it will attain equilibrium.
This can be written as:
$\dfrac{{{n}_{A}}\text{ x R}}{{{V}_{A}}(new)}=\dfrac{{{n}_{B}}\text{ x R}}{{{V}_{B}}(new)}$
Putting, the values in this, we get:
$\dfrac{5}{400(x)}=\dfrac{3}{300(x-4)}$
For solving x, we get:
$5(4-x)=4x$
${{V}_{A}}=x=\dfrac{20}{9}=2.22$
The volume of A after equilibrium will be 2.22 ${{m}^{3}}$.
Note: The formulas that we have used in the question, $n=\dfrac{PV}{TR}$, and $\dfrac{{{P}_{A}}}{{{T}_{A}}}=\dfrac{{{P}_{B}}}{{{T}_{B}}}$ can only be used because the condition was mentioned that the system is an ideal system, if the system is real then we cannot use these formulas.
Complete step-by-step answer: So according to Figure 1, in compartment A, the pressure is 5 bar, the volume is 1 ${{m}^{3}}$, and temperature 400 K. This can be written as:
${{P}_{A}}=5$
${{V}_{A}}=1$
${{T}_{1}}=400$
In compartment B, the pressure is 1 bar, the volume is 3 ${{m}^{3}}$, and temperature 400 K. This can be written as:
${{P}_{B}}=1$
${{V}_{B}}=3$
${{T}_{B}}=300$
So, from the given values we can calculate the number of moles for both the compartments by using the formula $n=\dfrac{PV}{TR}$, we get
${{n}_{A}}=\dfrac{\text{ 5 x 1}}{400\text{ x R}}=\dfrac{5}{400R}$
${{n}_{B}}=\dfrac{\text{ 1 x 3}}{300\text{ x R}}=\dfrac{3}{300R}$
The total volume will be = 1 + 3 = 4 ${{m}^{3}}$
In Figure 2, let us assume, the volume of A is x and volume of B is (4 – x).
We know that:
$\dfrac{{{P}_{A}}}{{{T}_{A}}}=\dfrac{{{P}_{B}}}{{{T}_{B}}}$, because it will attain equilibrium.
This can be written as:
$\dfrac{{{n}_{A}}\text{ x R}}{{{V}_{A}}(new)}=\dfrac{{{n}_{B}}\text{ x R}}{{{V}_{B}}(new)}$
Putting, the values in this, we get:
$\dfrac{5}{400(x)}=\dfrac{3}{300(x-4)}$
For solving x, we get:
$5(4-x)=4x$
${{V}_{A}}=x=\dfrac{20}{9}=2.22$
The volume of A after equilibrium will be 2.22 ${{m}^{3}}$.
Note: The formulas that we have used in the question, $n=\dfrac{PV}{TR}$, and $\dfrac{{{P}_{A}}}{{{T}_{A}}}=\dfrac{{{P}_{B}}}{{{T}_{B}}}$ can only be used because the condition was mentioned that the system is an ideal system, if the system is real then we cannot use these formulas.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




