
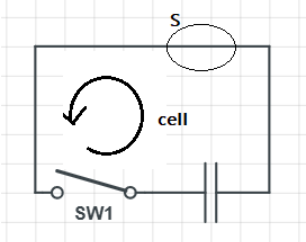
A closed surface $S$ is constructed around a conducting wire connected to a battery and a switch. As the switch is closed, the free electrons in the wire start moving along the wire. In any time interval, the number of electrons entering the closed surface $S$ is equal to the number of electrons leaving it. On closing the switch the flux of the electric field through the closed surface (more than ie option maybe correct).
A. is increased
B. is decreased
C. remains unchanged
D. zero

Answer
588k+ views
Hint: We need to find the charge in the closed surface $S$, clearly as $S$ covers some region of the connecting wires which carries some charge, we can say that the closed surface $S$ has some charge. We know that the total charge enclosed in a closed surface is given by Gauss law.
Formula:
$\Phi_{E}=\dfrac{q}{\epsilon_{0}}$
Complete answer:
From Gauss law, we know that the total electric flux through a closed surface is equal to $\dfrac{1}{\epsilon_{0}}$ times the charge enclosed in the surface, and it is given by
$\Phi_{E}=\dfrac{q}{\epsilon_{0}}$
Also an electric field $E$ is defined as the electric force $F$ per unit positive charge$q$, which is infinitesimally small and at rest, and is given as
$E=\dfrac{F}{q}$
Here, the closed surface $S$ is a part of the connecting wires. Then we have two cases, when the switch is open and the switch is closed.
When the switch is closed the charges keep moving through the surface. We can also say that the number of electrons leaving and entering $S$ at any given time is equal. Hence clearly, the surface $S$ doesn’t contain any charge.
Then the flux is given as $\Phi=\dfrac{0}{\epsilon_{0}}=0$
Then the electric flux is also zero.
When the switch is open, there is no flow of charges in the circuit, and hence no charge in $S$ also.
Then the flux is given as $\Phi=\dfrac{0}{\epsilon_{0}}=0$
Then again the electric flux is also zero, or the flux remains unchanged i.e. zero.
Hence the answer is C. remains unchanged and D. zero.
Note:
Gauss law can also be given as \[{{\Phi }_{_{E}}}=\mathop{{\int\!\!\!\!\!\int}\mkern-21mu \bigcirc}\nolimits_E
E\cdot dA \] where \[dA\] is the surface area vector. This form of Gauss law is called the integral form of Gauss law. Usually, the electric field of a point positive charge is radially outwards, whereas the electric field of a point negative charge is radially inwards to the charge. However, the electric field also depends on the symmetry of the charge carrying conductor.
Formula:
$\Phi_{E}=\dfrac{q}{\epsilon_{0}}$
Complete answer:
From Gauss law, we know that the total electric flux through a closed surface is equal to $\dfrac{1}{\epsilon_{0}}$ times the charge enclosed in the surface, and it is given by
$\Phi_{E}=\dfrac{q}{\epsilon_{0}}$
Also an electric field $E$ is defined as the electric force $F$ per unit positive charge$q$, which is infinitesimally small and at rest, and is given as
$E=\dfrac{F}{q}$
Here, the closed surface $S$ is a part of the connecting wires. Then we have two cases, when the switch is open and the switch is closed.
When the switch is closed the charges keep moving through the surface. We can also say that the number of electrons leaving and entering $S$ at any given time is equal. Hence clearly, the surface $S$ doesn’t contain any charge.
Then the flux is given as $\Phi=\dfrac{0}{\epsilon_{0}}=0$
Then the electric flux is also zero.
When the switch is open, there is no flow of charges in the circuit, and hence no charge in $S$ also.
Then the flux is given as $\Phi=\dfrac{0}{\epsilon_{0}}=0$
Then again the electric flux is also zero, or the flux remains unchanged i.e. zero.
Hence the answer is C. remains unchanged and D. zero.
Note:
Gauss law can also be given as \[{{\Phi }_{_{E}}}=\mathop{{\int\!\!\!\!\!\int}\mkern-21mu \bigcirc}\nolimits_E
E\cdot dA \] where \[dA\] is the surface area vector. This form of Gauss law is called the integral form of Gauss law. Usually, the electric field of a point positive charge is radially outwards, whereas the electric field of a point negative charge is radially inwards to the charge. However, the electric field also depends on the symmetry of the charge carrying conductor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




