
A circular disc of area ${{A}_{1}}$ is given; with its radius as the diameter of a circular disc of area ${{A}_{2}}$ is cut out. If the area of the remaining disc is denoted by ${{A}_{3}}$, then
(a) ${{A}_{1}}{{A}_{3}}<16A_{2}^{2}$
(b) ${{A}_{1}}{{A}_{3}}>16A_{2}^{2}$
(c) ${{A}_{1}}{{A}_{3}}=16A_{2}^{2}$
(d) ${{A}_{1}}{{A}_{3}}>2A_{2}^{2}$
Answer
611.4k+ views
Hint: Here, we will assume that the radius of the disc with area ${{A}_{1}}$ is R and then we will try to find the value of ${{A}_{2}}$ and ${{A}_{3}}$ in terms of R. After that we can try to check which of the relations provided in the option is the correct.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
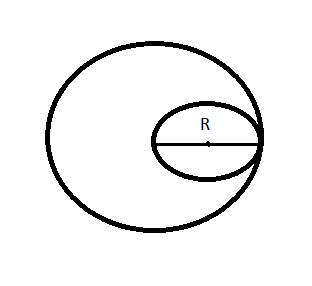
Let us consider that the radius of the circular disc whose area is ${{A}_{1}}$ is = R.
We know that the area of a disc is given by the formula $A=\pi \times {{\left( radius \right)}^{2}}$.
So, for the area of first disc we have:
${{A}_{1}}=\pi {{R}^{2}}............\left( 1 \right)$
Now, another disc whose area is ${{A}_{2}}$ is cut out from the disc of area ${{A}_{1}}$ as the radius of the second being the diameter of the first.
There, radius of the disc with area ${{A}_{2}}$ will be = $\dfrac{R}{2}$
So, for this disc area will be given as:
${{A}_{2}}=\pi \times {{\left( \dfrac{R}{2} \right)}^{2}}=\dfrac{\pi {{R}^{2}}}{4}............\left( 2 \right)$
Since, the area of the remaining disc is given as ${{A}_{3}}$ . So, we can write:
${{A}_{3}}={{A}_{1}}-{{A}_{2}}.............\left( 3 \right)$
On substituting the values of ${{A}_{1}}$ and ${{A}_{2}}$ from equation (1) and (2) in equation (3), we get:
$\begin{align}
& {{A}_{3}}=\pi {{R}^{2}}-\dfrac{\pi {{R}^{2}}}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow {{A}_{3}}=\dfrac{4\pi {{R}^{2}}-\pi {{R}^{2}}}{4}=\dfrac{3\pi {{R}^{2}}}{4} \\
\end{align}$
Now, to check the relations given in the options, we have to first find the values of ${{A}_{1}}{{A}_{3}}$.
We know that ${{A}_{1}}=\pi {{R}^{2}}$ and ${{A}_{3}}=\dfrac{3\pi {{R}^{2}}}{4}$.
Therefore, ${{A}_{1}}{{A}_{3}}=\pi {{R}^{2}}\times \dfrac{3\pi {{R}^{2}}}{4}=\dfrac{3{{\pi }^{2}}{{R}^{4}}}{4}$.
Also, we have to find the value of $16A_{2}^{2}$.
Since, ${{A}_{2}}=\dfrac{\pi {{R}^{2}}}{4}$.
Therefore, $16A_{2}^{2}=16\times \dfrac{{{\pi }^{2}}{{R}^{4}}}{16}={{\pi }^{2}}{{R}^{4}}$
Now, it is clear that $\dfrac{3{{\pi }^{2}}{{R}^{4}}}{4}<{{\pi }^{2}}{{R}^{4}}$.
So, ${{A}_{1}}{{A}_{3}}<16A_{2}^{2}$.
Now, to check for the last option, we have to calculate the value of $2A_{2}^{2}$ .
So, $2A_{2}^{2}=2\times {{\left( \dfrac{\pi {{R}^{2}}}{4} \right)}^{2}}=\dfrac{{{\pi }^{2}}{{R}^{4}}}{8}$
Since, $\dfrac{3{{\pi }^{2}}{{R}^{4}}}{4}>\dfrac{{{\pi }^{2}}{{R}^{4}}}{8}$
So, we have ${{A}_{1}}{{A}_{3}}>2A_{2}^{2}$.
Hence, option (a) and option (d) are the correct answers.
Note: Students should note here that we use the formula for the area of a circle to find the area of the disc. Students should be careful while comparing the area as they are in fractions to avoid unnecessary mistakes.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:

Let us consider that the radius of the circular disc whose area is ${{A}_{1}}$ is = R.
We know that the area of a disc is given by the formula $A=\pi \times {{\left( radius \right)}^{2}}$.
So, for the area of first disc we have:
${{A}_{1}}=\pi {{R}^{2}}............\left( 1 \right)$
Now, another disc whose area is ${{A}_{2}}$ is cut out from the disc of area ${{A}_{1}}$ as the radius of the second being the diameter of the first.
There, radius of the disc with area ${{A}_{2}}$ will be = $\dfrac{R}{2}$
So, for this disc area will be given as:
${{A}_{2}}=\pi \times {{\left( \dfrac{R}{2} \right)}^{2}}=\dfrac{\pi {{R}^{2}}}{4}............\left( 2 \right)$
Since, the area of the remaining disc is given as ${{A}_{3}}$ . So, we can write:
${{A}_{3}}={{A}_{1}}-{{A}_{2}}.............\left( 3 \right)$
On substituting the values of ${{A}_{1}}$ and ${{A}_{2}}$ from equation (1) and (2) in equation (3), we get:
$\begin{align}
& {{A}_{3}}=\pi {{R}^{2}}-\dfrac{\pi {{R}^{2}}}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow {{A}_{3}}=\dfrac{4\pi {{R}^{2}}-\pi {{R}^{2}}}{4}=\dfrac{3\pi {{R}^{2}}}{4} \\
\end{align}$
Now, to check the relations given in the options, we have to first find the values of ${{A}_{1}}{{A}_{3}}$.
We know that ${{A}_{1}}=\pi {{R}^{2}}$ and ${{A}_{3}}=\dfrac{3\pi {{R}^{2}}}{4}$.
Therefore, ${{A}_{1}}{{A}_{3}}=\pi {{R}^{2}}\times \dfrac{3\pi {{R}^{2}}}{4}=\dfrac{3{{\pi }^{2}}{{R}^{4}}}{4}$.
Also, we have to find the value of $16A_{2}^{2}$.
Since, ${{A}_{2}}=\dfrac{\pi {{R}^{2}}}{4}$.
Therefore, $16A_{2}^{2}=16\times \dfrac{{{\pi }^{2}}{{R}^{4}}}{16}={{\pi }^{2}}{{R}^{4}}$
Now, it is clear that $\dfrac{3{{\pi }^{2}}{{R}^{4}}}{4}<{{\pi }^{2}}{{R}^{4}}$.
So, ${{A}_{1}}{{A}_{3}}<16A_{2}^{2}$.
Now, to check for the last option, we have to calculate the value of $2A_{2}^{2}$ .
So, $2A_{2}^{2}=2\times {{\left( \dfrac{\pi {{R}^{2}}}{4} \right)}^{2}}=\dfrac{{{\pi }^{2}}{{R}^{4}}}{8}$
Since, $\dfrac{3{{\pi }^{2}}{{R}^{4}}}{4}>\dfrac{{{\pi }^{2}}{{R}^{4}}}{8}$
So, we have ${{A}_{1}}{{A}_{3}}>2A_{2}^{2}$.
Hence, option (a) and option (d) are the correct answers.
Note: Students should note here that we use the formula for the area of a circle to find the area of the disc. Students should be careful while comparing the area as they are in fractions to avoid unnecessary mistakes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




