
A circular coil of radius 10 cm and 25 turns is rotated about its vertical diameter with an angular speed of $40 \dfrac{rad}{s}$, in a uniform horizontal magnetic field of magnitude $5\times 10^{-2}T$. Calculate the maximum emf induced in the coil. Also, find the current in the coil if the resistance of the coil is $15 \Omega$ .
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: The concept of electromagnetic induction has to be applied. Use the faraday's law to get the variation of the induced emf due to the rotation of the Coil. Consider the peak value of the induced emf. To find the current in the coil use ohm's law in the coil.
Complete answer:
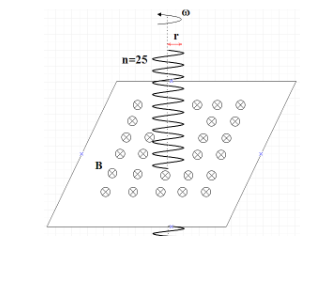
Given radius of coil r = 10cm
Number of turns in a circular coil N = 25
The angular speed of the coil omega = $40 \dfrac{rad}{s}$
The magnitude of a uniform horizontal magnetic field $B = 5\times 10^{-2}$
Area of the coil $A=\pi {{r}^{2}}=3.14\times {{(10\times {{10}^{-2}})}^{2}}=0.0314{{m}^{2}}$
The resistance of the coil $R=15\Omega $
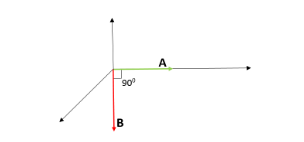
Now, to find the induced emf, we need magnetic flux.
Magnetic flux is given by the equation,
$\phi =\overrightarrow{B}\cdot \overrightarrow{A}=BA\cos \left( \theta \right)$
But, from the figure, we can understand that the angle between the area vector and the magnetic field is $90{}^\circ $ .
Therefore, $\phi =\overrightarrow{B}\cdot \overrightarrow{A}=BA$ .
Now we need to calculate the induced emf in the coil. It is given by,
$E_{induced} = \dfrac{-d\phi}{dt} = -NB\dfrac{dA}{dt} = -NBA\omega$
Where $\dfrac{dA}{dt}$ refers to the rate at which the area vector rotates which is nothing but the $\omega$ given.
So we can get the induced emf as,
$E_{induced} = -NBA\omega = 25(5\times 10^{-2})\times (3.14\times (10\times 10^{-2})^2)\times 40 = 1.57 V$
Thus we got the induced emf using the faraday law of induction as $E_{induced} = 1.57 V$ .
Consequently, the value of the current in the circuit can be calculated as using the ohms law as,
$I = \dfrac{V}{R} = \dfrac{1.57}{15} = 0.1047 A$
So we finally found the value of the current as $I = 0.1047 A$ using ohm’s law.
Additional Information:
Here the coil is rotating in the magnetic field which is constant. We can consider that the area vector of the coil is rotating the given angular speed and hence the derivative of the Area vector is cos term with amplitude $NAB\omega$ which we used in the problem.
Note:
We can solve the above in a different assuming that the loop is stationary and the field is rotating then in that case we need to evaluate the value of $\dfrac{dB}{dt}$ which is time-consuming and hence we have used the concept of the variable area vector to get the max value of the induced emf and then found the current.
Complete answer:

Given radius of coil r = 10cm
Number of turns in a circular coil N = 25
The angular speed of the coil omega = $40 \dfrac{rad}{s}$
The magnitude of a uniform horizontal magnetic field $B = 5\times 10^{-2}$
Area of the coil $A=\pi {{r}^{2}}=3.14\times {{(10\times {{10}^{-2}})}^{2}}=0.0314{{m}^{2}}$
The resistance of the coil $R=15\Omega $

Now, to find the induced emf, we need magnetic flux.
Magnetic flux is given by the equation,
$\phi =\overrightarrow{B}\cdot \overrightarrow{A}=BA\cos \left( \theta \right)$
But, from the figure, we can understand that the angle between the area vector and the magnetic field is $90{}^\circ $ .
Therefore, $\phi =\overrightarrow{B}\cdot \overrightarrow{A}=BA$ .
Now we need to calculate the induced emf in the coil. It is given by,
$E_{induced} = \dfrac{-d\phi}{dt} = -NB\dfrac{dA}{dt} = -NBA\omega$
Where $\dfrac{dA}{dt}$ refers to the rate at which the area vector rotates which is nothing but the $\omega$ given.
So we can get the induced emf as,
$E_{induced} = -NBA\omega = 25(5\times 10^{-2})\times (3.14\times (10\times 10^{-2})^2)\times 40 = 1.57 V$
Thus we got the induced emf using the faraday law of induction as $E_{induced} = 1.57 V$ .
Consequently, the value of the current in the circuit can be calculated as using the ohms law as,
$I = \dfrac{V}{R} = \dfrac{1.57}{15} = 0.1047 A$
So we finally found the value of the current as $I = 0.1047 A$ using ohm’s law.
Additional Information:
Here the coil is rotating in the magnetic field which is constant. We can consider that the area vector of the coil is rotating the given angular speed and hence the derivative of the Area vector is cos term with amplitude $NAB\omega$ which we used in the problem.
Note:
We can solve the above in a different assuming that the loop is stationary and the field is rotating then in that case we need to evaluate the value of $\dfrac{dB}{dt}$ which is time-consuming and hence we have used the concept of the variable area vector to get the max value of the induced emf and then found the current.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




