
A circle with radius \[\left| a \right|\] and centre on y-axis slides along it and a variable line though \[\left( {a,0} \right)\] cuts the circle at points \[P\] and \[Q\]. The region in which the point of intersection of tangents to the circle at points \[P\] and \[Q\] lies is represented by
A. \[{y^2} \geqslant 4\left( {ax - {a^2}} \right)\]
B. \[{y^2} \leqslant 4\left( {ax - {a^2}} \right)\]
C. \[y \geqslant 4\left( {ax - {a^2}} \right)\]
D. \[y \leqslant 4\left( {ax - {a^2}} \right)\]
Answer
623.1k+ views
Hint: First of all, consider the centre of the circle as a variable on the y-axis and find the equation of the circle. Then find the equation of chord of contact at points \[P\] and \[Q\]. As the value of the y-coordinate of the centre of the circle is real, equate the value of discriminant to greater than or equal to zero.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given radius of the circle is \[\left| a \right|\]
Let \[\left( {0,\alpha } \right)\] be the centre of the circle as the centre lies on the y-axis.
We know that the equation of the circle with centre \[\left( {h,k} \right)\] and radius \[r\] is given by \[{\left( {x - h} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - k} \right)^2} = {r^2}\].
So, the given circle equation is given by
\[
{\left( {x - 0} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - \alpha } \right)^2} = {\left( {\left| a \right|} \right)^2} \\
{x^2} + {\left( {y - \alpha } \right)^2} = {a^2} \\
{x^2} + {y^2} - 2\alpha y + {\alpha ^2} - {a^2} = 0 \\
{x^2} + {y^2} - 2\alpha y + \left( {{\alpha ^2} - {a^2}} \right) = 0 \\
\]
Let \[R\left( {h,k} \right)\] be the point of intersection of the tangents to the circle at points \[P\] and \[Q\] as shown in the below figure:
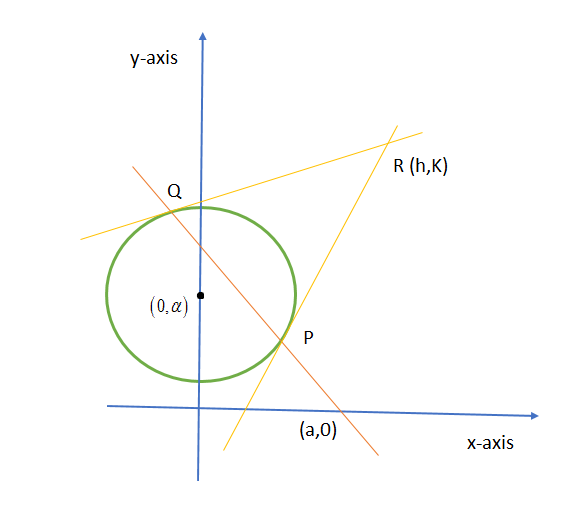
We know that the equation of chord of contact at \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\] to the circle \[{x^2} + {y^2} + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0\] is given by \[x{x_1} + y{y_1} + g\left( {x + {x_1}} \right) + f\left( {y + {y_1}} \right) + c = 0\].
So, the equation of chord of contact i.e., equation of PQ is given by
\[
xh + yk + 0\left( {x + h} \right) + \left( { - \alpha } \right)\left( {y + k} \right) + \left( {{\alpha ^2} - {a^2}} \right) = 0 \\
xh + yk - \alpha \left( {y + k} \right) + \left( {{\alpha ^2} - {a^2}} \right) = 0 \\
\]
But this equation is passing through \[\left( {a,0} \right)\]. So, this point should satisfy the equation PQ.
\[
ah + \left( 0 \right)k - \alpha \left( {0 + k} \right) + \left( {{\alpha ^2} - {a^2}} \right) = 0 \\
ah - \alpha k + {\alpha ^2} - {a^2} = 0 \\
{\alpha ^2} - \alpha k + ah - {a^2} = 0 \\
\]
We know that for the equation \[a{x^2} + bx + c = 0\] if \[x\] is a real value then its discriminant must be greater than or equal to zero i.e., \[{b^2} - 4ac \geqslant 0\].
In the equation \[{\alpha ^2} - \alpha k + ah - {a^2} = 0\] as \[\alpha \] is a real since it is a variable and lies on y-axis its discriminant must be greater than equal to zero.
So, we have
\[
{\left( { - k} \right)^2} - 4\left( 1 \right)\left( {ah - {a^2}} \right) \geqslant 0 \\
{k^2} - 4\left( {ah - {a^2}} \right) \geqslant 0 \\
{k^2} \geqslant 4\left( {ah - {a^2}} \right) \\
\]
As we have to find the coordinates of \[\left( {h,k} \right)\], we substitute \[h = x\] and \[k = y\], then we get
\[{y^2} \geqslant 4\left( {ax - {a^2}} \right)\]
Thus, the correct option is A. \[{y^2} \geqslant 4\left( {ax - {a^2}} \right)\]
Note: The chord joining the points of contact of the two tangents to a conic drawn from a given point, outside it, is called the chord of contact. For the equation \[a{x^2} + bx + c = 0\] if \[x\] is a real value then its discriminant must be greater than or equal to zero i.e., \[{b^2} - 4ac \geqslant 0\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given radius of the circle is \[\left| a \right|\]
Let \[\left( {0,\alpha } \right)\] be the centre of the circle as the centre lies on the y-axis.
We know that the equation of the circle with centre \[\left( {h,k} \right)\] and radius \[r\] is given by \[{\left( {x - h} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - k} \right)^2} = {r^2}\].
So, the given circle equation is given by
\[
{\left( {x - 0} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - \alpha } \right)^2} = {\left( {\left| a \right|} \right)^2} \\
{x^2} + {\left( {y - \alpha } \right)^2} = {a^2} \\
{x^2} + {y^2} - 2\alpha y + {\alpha ^2} - {a^2} = 0 \\
{x^2} + {y^2} - 2\alpha y + \left( {{\alpha ^2} - {a^2}} \right) = 0 \\
\]
Let \[R\left( {h,k} \right)\] be the point of intersection of the tangents to the circle at points \[P\] and \[Q\] as shown in the below figure:

We know that the equation of chord of contact at \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\] to the circle \[{x^2} + {y^2} + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0\] is given by \[x{x_1} + y{y_1} + g\left( {x + {x_1}} \right) + f\left( {y + {y_1}} \right) + c = 0\].
So, the equation of chord of contact i.e., equation of PQ is given by
\[
xh + yk + 0\left( {x + h} \right) + \left( { - \alpha } \right)\left( {y + k} \right) + \left( {{\alpha ^2} - {a^2}} \right) = 0 \\
xh + yk - \alpha \left( {y + k} \right) + \left( {{\alpha ^2} - {a^2}} \right) = 0 \\
\]
But this equation is passing through \[\left( {a,0} \right)\]. So, this point should satisfy the equation PQ.
\[
ah + \left( 0 \right)k - \alpha \left( {0 + k} \right) + \left( {{\alpha ^2} - {a^2}} \right) = 0 \\
ah - \alpha k + {\alpha ^2} - {a^2} = 0 \\
{\alpha ^2} - \alpha k + ah - {a^2} = 0 \\
\]
We know that for the equation \[a{x^2} + bx + c = 0\] if \[x\] is a real value then its discriminant must be greater than or equal to zero i.e., \[{b^2} - 4ac \geqslant 0\].
In the equation \[{\alpha ^2} - \alpha k + ah - {a^2} = 0\] as \[\alpha \] is a real since it is a variable and lies on y-axis its discriminant must be greater than equal to zero.
So, we have
\[
{\left( { - k} \right)^2} - 4\left( 1 \right)\left( {ah - {a^2}} \right) \geqslant 0 \\
{k^2} - 4\left( {ah - {a^2}} \right) \geqslant 0 \\
{k^2} \geqslant 4\left( {ah - {a^2}} \right) \\
\]
As we have to find the coordinates of \[\left( {h,k} \right)\], we substitute \[h = x\] and \[k = y\], then we get
\[{y^2} \geqslant 4\left( {ax - {a^2}} \right)\]
Thus, the correct option is A. \[{y^2} \geqslant 4\left( {ax - {a^2}} \right)\]
Note: The chord joining the points of contact of the two tangents to a conic drawn from a given point, outside it, is called the chord of contact. For the equation \[a{x^2} + bx + c = 0\] if \[x\] is a real value then its discriminant must be greater than or equal to zero i.e., \[{b^2} - 4ac \geqslant 0\].
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction




