
A circle touches the axes at the point \[\left( 3,0 \right)\] and \[\left( 0,-3 \right)\]. The centre of the circle is
a)\[\left( 3,-3 \right)\]
b)\[\left( 0,0 \right)\]
c)\[\left( -3,0 \right)\]
d)\[\left( 6,-6 \right)\]
Answer
627.6k+ views
Hint: Use the fact that if the circle touches both the coordinate axes, then distance between the centre of the circle and the points at which the circle touches the coordinate axes is equal and is equal to the radius of the circle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have a circle which touches both the coordinate axes at points \[\left( 3,0 \right)\] and \[\left( 0,-3 \right)\].
We want to find the centre of the circle.
Let’s assume that the centre of the circle is at any point \[\left( h,k \right)\].
We know that the distance between the centre of the circle and the points at which the circle touch the coordinate axes is equal and is equal to the radius of the circle.
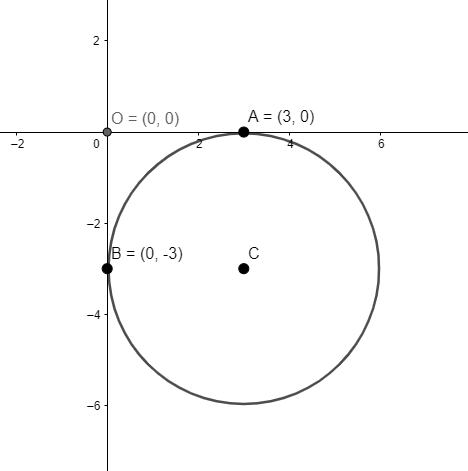
In the figure above, we observe that as lines \[AO\] and \[BC\] are parallel and are of equal length which is equal to the radius of the circle.
Thus, distance between \[C\left( h,k \right)\] and \[B\left( -0,-3 \right)\] is same as distance between \[A\left( 3,0 \right)\] and \[O\left( 0,0 \right)\] which is equal to the radius of the circle.
We know that distance between any two points of the form \[\left( a,b \right)\] and \[\left( c,d \right)\] is \[\sqrt{{{\left( a-c \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( b-d \right)}^{2}}}\].
Substituting \[a=0,b=3,c=0,d=0\] in the above equation, we get distance between \[A\left( 3,0 \right)\] and \[O\left( 0,0 \right)\] is \[\sqrt{{{\left( 0-0 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 3-0 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{3}^{2}}}=3\] units which is the radius of the circle.
Substituting \[a=h,b=k,c=0,d=-3\] in the distance formula, we get \[\sqrt{{{\left( h-0 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( k+3 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{\left( h \right)}^{2}}+{{(k+3)}^{2}}}\] as the distance between points \[C\left( h,k \right)\] and \[B\left( 0,-3 \right)\].
We know that this distance is equal to the radius of the circle which is \[3\] units.
Substituting \[a=h,b=k,c=3,d=0\] in the distance formula, we get \[\sqrt{{{\left( h-3 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( k+0 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{\left( h-3 \right)}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}}\] as the distance between points \[C\left( h,k \right)\] and \[A\left( 3,0 \right)\].
We know that this distance is equal to the radius of the circle which is \[3\] units.
Thus, we have \[\sqrt{{{\left( h \right)}^{2}}+{{(k+3)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{\left( h-3 \right)}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}}=3\].
Solving first two equations by squaring them, we get \[{{h}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}+9+6k={{h}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}+9-6h\].
\[\Rightarrow k=-h\] \[...\left( 1 \right)\]
Substituting equation \[\left( 1 \right)\] in the equation \[\sqrt{{{\left( h-3 \right)}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}}=3\], we get \[\sqrt{{{\left( h-3 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -h \right)}^{2}}}=3\].
Solving the equation by squaring on both sides, we get \[2{{h}^{2}}-6h=0\].
\[\Rightarrow 2h\left( h-3 \right)=0\]
Thus, we have \[h=3\] as we will reject \[h=0\] because it will give us origin which doesn’t lie in the circle.
So, we get \[k=-3\].
Thus, the centre of the circle is \[\left( h,k \right)=\left( 3,-3 \right)\].
Hence, the correct answer is \[\left( 3,-3 \right)\].
Answer is Option (a).
Note: It is necessary to draw the figure and observe that the distance between the centre of the circle and the points at which the circle touches the coordinate axes is equal and is equal to the radius of the circle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have a circle which touches both the coordinate axes at points \[\left( 3,0 \right)\] and \[\left( 0,-3 \right)\].
We want to find the centre of the circle.
Let’s assume that the centre of the circle is at any point \[\left( h,k \right)\].
We know that the distance between the centre of the circle and the points at which the circle touch the coordinate axes is equal and is equal to the radius of the circle.

In the figure above, we observe that as lines \[AO\] and \[BC\] are parallel and are of equal length which is equal to the radius of the circle.
Thus, distance between \[C\left( h,k \right)\] and \[B\left( -0,-3 \right)\] is same as distance between \[A\left( 3,0 \right)\] and \[O\left( 0,0 \right)\] which is equal to the radius of the circle.
We know that distance between any two points of the form \[\left( a,b \right)\] and \[\left( c,d \right)\] is \[\sqrt{{{\left( a-c \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( b-d \right)}^{2}}}\].
Substituting \[a=0,b=3,c=0,d=0\] in the above equation, we get distance between \[A\left( 3,0 \right)\] and \[O\left( 0,0 \right)\] is \[\sqrt{{{\left( 0-0 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 3-0 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{3}^{2}}}=3\] units which is the radius of the circle.
Substituting \[a=h,b=k,c=0,d=-3\] in the distance formula, we get \[\sqrt{{{\left( h-0 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( k+3 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{\left( h \right)}^{2}}+{{(k+3)}^{2}}}\] as the distance between points \[C\left( h,k \right)\] and \[B\left( 0,-3 \right)\].
We know that this distance is equal to the radius of the circle which is \[3\] units.
Substituting \[a=h,b=k,c=3,d=0\] in the distance formula, we get \[\sqrt{{{\left( h-3 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( k+0 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{\left( h-3 \right)}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}}\] as the distance between points \[C\left( h,k \right)\] and \[A\left( 3,0 \right)\].
We know that this distance is equal to the radius of the circle which is \[3\] units.
Thus, we have \[\sqrt{{{\left( h \right)}^{2}}+{{(k+3)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{\left( h-3 \right)}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}}=3\].
Solving first two equations by squaring them, we get \[{{h}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}+9+6k={{h}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}+9-6h\].
\[\Rightarrow k=-h\] \[...\left( 1 \right)\]
Substituting equation \[\left( 1 \right)\] in the equation \[\sqrt{{{\left( h-3 \right)}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}}=3\], we get \[\sqrt{{{\left( h-3 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -h \right)}^{2}}}=3\].
Solving the equation by squaring on both sides, we get \[2{{h}^{2}}-6h=0\].
\[\Rightarrow 2h\left( h-3 \right)=0\]
Thus, we have \[h=3\] as we will reject \[h=0\] because it will give us origin which doesn’t lie in the circle.
So, we get \[k=-3\].
Thus, the centre of the circle is \[\left( h,k \right)=\left( 3,-3 \right)\].
Hence, the correct answer is \[\left( 3,-3 \right)\].
Answer is Option (a).
Note: It is necessary to draw the figure and observe that the distance between the centre of the circle and the points at which the circle touches the coordinate axes is equal and is equal to the radius of the circle.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Who is known as the "Little Master" in Indian cricket history?

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

Who Won 36 Oscar Awards? Record Holder Revealed

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE




