
A car travelling at $60\,kmh{r^{ - 1}}$ overtake another car travelling at $42\,kmh{r^{ - 1}}$. Assuming each car to be $5.0\,m$ long. Find the time, taken during the overtaking and the total road distance used for overtaking?
Answer
588.3k+ views
Hint: For this type of problems, we have to find the relative velocity between two moving objects and the relative distance travelled by the overtaking car. The velocity, distance and time relation formula is used to determine the time taken and total distance travelled by the overtaking car.
Formula used:
Velocity formula,
$v = \dfrac{d}{t}$
Where,
$v$ is the velocity of the car, $d$ is the distance travelled by car, $t$ is the time taken by the car.
Complete step by step answer:
Given that,
Speed of the first car is $60\,kmh{r^{ - 1}}$
For the unit conversion from $kmh{r^{ - 1}}$ to $m{s^{ - 1}}$, we have to multiply the speed value with $\dfrac{5}{{18}}$
So, velocity of the first car,
${v_1} = 60 \times \dfrac{5}{{18}}\,m{s^{ - 1}}$
On simplifying,
$\Rightarrow {v_1} = \dfrac{{50}}{3}\,m{s^{ - 1}}$
Similarly, for the velocity of second car,
Velocity of the second car,
${v_2} = 42 \times \dfrac{5}{{18}}\,m{s^{ - 1}}$
On simplifying,
$\Rightarrow {v_2} = \dfrac{{35}}{3}\,m{s^{ - 1}}$
The length of each car is $5\,m$
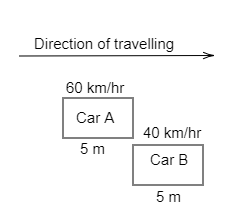
If the first car overtakes the second car, then we have to find the relative velocity of the two cars by,
${v_{12}} = {v_1} - {v_2}\,.................\left( 1 \right)$
Where,
${v_{12}}$ is the relative velocity of the two cars
${v_1}$ is the velocity of the first car
${v_2}$ is the velocity of the second car
Substituting the velocity value of the first and second car in the equation (1),
$\Rightarrow {v_{12}} = \dfrac{{50}}{3} - \dfrac{{35}}{3}$
On subtracting, the above equation can be written as,
$\Rightarrow {v_{12}} = \dfrac{{15}}{3}$
On further calculations,
$\Rightarrow {v_{12}} = 5\,m{s^{ - 1}}$
So, the relative velocity is $5\,m{s^{ - 1}}$.
The distance travelled by the first car to overtake the second car is the sum of the length of the two cars,
$d = {l_1} + {l_2}$
Where,
$d$ is the distance travelled by the first car to overtake the second car
${l_1}$ is the length of the first car
${l_2}$ is the length of the second car
$
\Rightarrow d = 5 + 5 \\
\Rightarrow d = 10\,m \\
$
By using velocity formula,
$v = \dfrac{d}{t}$
We need to find the time, so keep the time $\left( t \right)$ in one side and other term in other side, the above equation can be written as,
$\Rightarrow t = \dfrac{d}{v}$
Substitute the distance travelled by the first car to overtake second car and the relative velocity value in the above equation,
$\Rightarrow t = \dfrac{{10}}{5}$
On simplifying,
$\Rightarrow t = 2\,s$
Therefore, the time taken for the first car to overtake the second car is $2\,s$.
Then the distance travelled by the first car to overtake the second car is,
$d = v \times t$
Here,
$d$ is the distance travelled by the first car
$v$ is the velocity of the first car
$t$ is the time take to overtake the second car
Substituting the velocity and time value in the above equation,
$\Rightarrow d = \dfrac{{50}}{3} \times 2$
On simplifying,
$\Rightarrow d = 33.3\,m$
The total distance for overtaking is the sum of distance travelled by the first car and the length of the second car.
Total road distance used for overtake is $33.3 + 5 = 38.3\,m$
$\therefore $ The time taken for overtaking is $2\,s$ and the total road distance used for overtaking is $38.3\,m$
Note:
In given data, the speed of the car is given. So, we have to convert the speed into velocity before the calculation. The speed is converted to velocity by multiplying the speed with $\dfrac{5}{{18}}$. In relative velocity, the first car is overtaking the second car, so the velocity of the first car is subtracted from the velocity of the second car.
Formula used:
Velocity formula,
$v = \dfrac{d}{t}$
Where,
$v$ is the velocity of the car, $d$ is the distance travelled by car, $t$ is the time taken by the car.
Complete step by step answer:
Given that,
Speed of the first car is $60\,kmh{r^{ - 1}}$
For the unit conversion from $kmh{r^{ - 1}}$ to $m{s^{ - 1}}$, we have to multiply the speed value with $\dfrac{5}{{18}}$
So, velocity of the first car,
${v_1} = 60 \times \dfrac{5}{{18}}\,m{s^{ - 1}}$
On simplifying,
$\Rightarrow {v_1} = \dfrac{{50}}{3}\,m{s^{ - 1}}$
Similarly, for the velocity of second car,
Velocity of the second car,
${v_2} = 42 \times \dfrac{5}{{18}}\,m{s^{ - 1}}$
On simplifying,
$\Rightarrow {v_2} = \dfrac{{35}}{3}\,m{s^{ - 1}}$
The length of each car is $5\,m$

If the first car overtakes the second car, then we have to find the relative velocity of the two cars by,
${v_{12}} = {v_1} - {v_2}\,.................\left( 1 \right)$
Where,
${v_{12}}$ is the relative velocity of the two cars
${v_1}$ is the velocity of the first car
${v_2}$ is the velocity of the second car
Substituting the velocity value of the first and second car in the equation (1),
$\Rightarrow {v_{12}} = \dfrac{{50}}{3} - \dfrac{{35}}{3}$
On subtracting, the above equation can be written as,
$\Rightarrow {v_{12}} = \dfrac{{15}}{3}$
On further calculations,
$\Rightarrow {v_{12}} = 5\,m{s^{ - 1}}$
So, the relative velocity is $5\,m{s^{ - 1}}$.
The distance travelled by the first car to overtake the second car is the sum of the length of the two cars,
$d = {l_1} + {l_2}$
Where,
$d$ is the distance travelled by the first car to overtake the second car
${l_1}$ is the length of the first car
${l_2}$ is the length of the second car
$
\Rightarrow d = 5 + 5 \\
\Rightarrow d = 10\,m \\
$
By using velocity formula,
$v = \dfrac{d}{t}$
We need to find the time, so keep the time $\left( t \right)$ in one side and other term in other side, the above equation can be written as,
$\Rightarrow t = \dfrac{d}{v}$
Substitute the distance travelled by the first car to overtake second car and the relative velocity value in the above equation,
$\Rightarrow t = \dfrac{{10}}{5}$
On simplifying,
$\Rightarrow t = 2\,s$
Therefore, the time taken for the first car to overtake the second car is $2\,s$.
Then the distance travelled by the first car to overtake the second car is,
$d = v \times t$
Here,
$d$ is the distance travelled by the first car
$v$ is the velocity of the first car
$t$ is the time take to overtake the second car
Substituting the velocity and time value in the above equation,
$\Rightarrow d = \dfrac{{50}}{3} \times 2$
On simplifying,
$\Rightarrow d = 33.3\,m$
The total distance for overtaking is the sum of distance travelled by the first car and the length of the second car.
Total road distance used for overtake is $33.3 + 5 = 38.3\,m$
$\therefore $ The time taken for overtaking is $2\,s$ and the total road distance used for overtaking is $38.3\,m$
Note:
In given data, the speed of the car is given. So, we have to convert the speed into velocity before the calculation. The speed is converted to velocity by multiplying the speed with $\dfrac{5}{{18}}$. In relative velocity, the first car is overtaking the second car, so the velocity of the first car is subtracted from the velocity of the second car.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




