
A car is moving on a straight road with uniform acceleration. The speed of car varies with time as follows:
Speed(m/s) 5 10 15 20 25 30 Time(s) 0 10 20 30 40 50
Draw the speed time graph by choosing a convenient scale. Calculate
(i) Acceleration of the car
(ii) Distance travelled by the car in 10 seconds.
| Speed(m/s) | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 |
| Time(s) | 0 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 |
Answer
572.7k+ views
Hint:Here, we take speed and time as X and Y axis respectively, unit scale of 5m for axis and 10 seconds for Y axis and plot the points in the graph. Using any two initial and final velocities from the table and with their respective times; we will apply first the kinematic equation of linear motion to find the acceleration and then the third equation of kinematics to find the distance travelled.
Complete step by step answer:
(i) Here, as the car is moving with a uniform acceleration, we can apply the three equations of kinematics for an object performing a linear motion. Now, here, from the values of speed of the car and the time required to achieve the particular speed, the graph obtained from these values is shown as below:
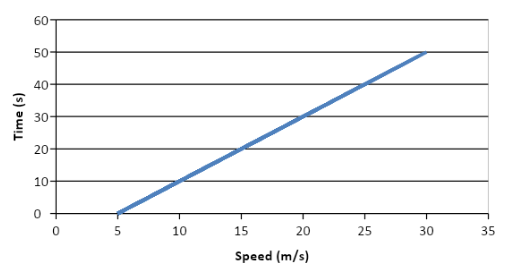
Here, as the car is moving in with a uniform acceleration, the speed time graph of the car is linear as shown in the figure. Now, we need to find the acceleration of the car. The acceleration of the car can be obtained from the first equation of linear motion as below:
\[v = u + at\]
Here, v is the final velocity, u is the initial velocity, u is the initial velocity, a is the uniform acceleration and t is the time taken by the car.
So for the time period of 0 to 10 seconds, we put the values of their velocities, gain the uniform acceleration as follows:
\[
10=5+a\centerdot 10 \\
\therefore a=0.5\,m/{s^2} \\
\]
(ii) Now, to obtain the distance travelled by the car in 10 seconds, we will from the third equation of linear motion for uniform acceleration as follows:
\[{v^2} - {u^2} = 2ad\]
Here, d is the distance travelled by the car. For 10 seconds, the value of the distance travelled will be given as follows:
\[
{10^2} - {5^2} = 2(0.5)d \\
\therefore d = 75m \\
\]
Thus the distance travelled is $75$ meters and uniform acceleration is \[0.5\,m/{s^2}\].
Note: Another way to find the distance travelled is using the second kinematic equation of linear motion\[d = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\], where u is taken as 10, for 10 seconds, and we will put negative sign in between and obtain the answer 75 meters in this way by also putting the value of\[a = 0.5\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}}\]. These equations can only be used for constant acceleration.
Complete step by step answer:
(i) Here, as the car is moving with a uniform acceleration, we can apply the three equations of kinematics for an object performing a linear motion. Now, here, from the values of speed of the car and the time required to achieve the particular speed, the graph obtained from these values is shown as below:

Here, as the car is moving in with a uniform acceleration, the speed time graph of the car is linear as shown in the figure. Now, we need to find the acceleration of the car. The acceleration of the car can be obtained from the first equation of linear motion as below:
\[v = u + at\]
Here, v is the final velocity, u is the initial velocity, u is the initial velocity, a is the uniform acceleration and t is the time taken by the car.
So for the time period of 0 to 10 seconds, we put the values of their velocities, gain the uniform acceleration as follows:
\[
10=5+a\centerdot 10 \\
\therefore a=0.5\,m/{s^2} \\
\]
(ii) Now, to obtain the distance travelled by the car in 10 seconds, we will from the third equation of linear motion for uniform acceleration as follows:
\[{v^2} - {u^2} = 2ad\]
Here, d is the distance travelled by the car. For 10 seconds, the value of the distance travelled will be given as follows:
\[
{10^2} - {5^2} = 2(0.5)d \\
\therefore d = 75m \\
\]
Thus the distance travelled is $75$ meters and uniform acceleration is \[0.5\,m/{s^2}\].
Note: Another way to find the distance travelled is using the second kinematic equation of linear motion\[d = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\], where u is taken as 10, for 10 seconds, and we will put negative sign in between and obtain the answer 75 meters in this way by also putting the value of\[a = 0.5\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}}\]. These equations can only be used for constant acceleration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE




