
A car is moving on a curved road of radius R. The road is banked at an angle $\theta $. The coefficient of friction between the tyres of the car and the road is ${\mu _S}$. The maximum safe velocity on this road is:
$
{\text{A}}{\text{. }}\sqrt {g{R^2}\dfrac{{{\mu _S} + \tan \theta }}{{1 - {\mu _S}\tan \theta }}} \\
{\text{B}}{\text{. }}\sqrt {gR\dfrac{{{\mu _S} + \tan \theta }}{{1 - {\mu _S}\tan \theta }}} \\
{\text{C}}{\text{. }}\sqrt {\dfrac{g}{R}\dfrac{{{\mu _S} + \tan \theta }}{{1 - {\mu _S}\tan \theta }}} \\
{\text{D}}{\text{. }}\sqrt {\dfrac{g}{{{R^2}}}\dfrac{{{\mu _S} + \tan \theta }}{{1 - {\mu _S}\tan \theta }}} \\
$
Answer
579k+ views
Hint: First of all, we need to draw a free body diagram for the car moving on the curved road showing the frictional force, force due to weight and the normal reaction force acting on the car. Then by obtaining equations of motion from the diagram and solving them for velocity, we can get the required answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given a car which is moving on a curve of radius R. The road is banked at an angle $\theta $. The coefficient of friction between the tyres of the car and the road is given as ${\mu _S}$. Based on this information, we can draw the following free body diagram which shows the road banked at the given angle.
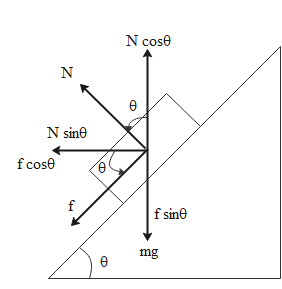
In the diagram, we have the weight of the car mg, normal reaction force N and the frictional force f between road and car and their components. From the diagram, we can see that the following components can be equated in their magnitude.
\[
N\cos \theta = mg + f\sin \theta \\
N\cos \theta - f\sin \theta = mg{\text{ }}...{\text{(i)}} \\
N\sin \theta + f\cos \theta = \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R}{\text{ }}...{\text{(ii)}} \\
\]
Now we can divide equation (ii) by equation (i). Doing so, we get
$\dfrac{{{v^2}}}{{Rg}} = \dfrac{{N\sin \theta + f\cos \theta }}{{N\cos \theta - f\sin \theta }}$ …(iii)
We can write the expression for the friction force as follows:
$
f = {\mu _S}N \\
\Rightarrow {\mu _S} = \dfrac{f}{N} \\
$
Using this in equation (iii), we get
$
\dfrac{{{v^2}}}{{Rg}} = \dfrac{{\sin \theta + {\mu _S}\cos \theta }}{{\cos \theta - {\mu _S}\sin \theta }} \\
\Rightarrow v = \sqrt {Rg\left( {\dfrac{{\sin \theta + {\mu _S}\cos \theta }}{{\cos \theta - {\mu _S}\sin \theta }}} \right)} \\
$
This is the required expression for the velocity of the car. Hence, the correct answer is option B.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: It should be noted that we have written the second equation on the basis of the fact that the horizontal component of the normal reaction force provides the necessary centripetal force required to move the car on the curved turn of the road. While moving on the curved road, the car requires a centripetal force to move in a curve.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given a car which is moving on a curve of radius R. The road is banked at an angle $\theta $. The coefficient of friction between the tyres of the car and the road is given as ${\mu _S}$. Based on this information, we can draw the following free body diagram which shows the road banked at the given angle.

In the diagram, we have the weight of the car mg, normal reaction force N and the frictional force f between road and car and their components. From the diagram, we can see that the following components can be equated in their magnitude.
\[
N\cos \theta = mg + f\sin \theta \\
N\cos \theta - f\sin \theta = mg{\text{ }}...{\text{(i)}} \\
N\sin \theta + f\cos \theta = \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R}{\text{ }}...{\text{(ii)}} \\
\]
Now we can divide equation (ii) by equation (i). Doing so, we get
$\dfrac{{{v^2}}}{{Rg}} = \dfrac{{N\sin \theta + f\cos \theta }}{{N\cos \theta - f\sin \theta }}$ …(iii)
We can write the expression for the friction force as follows:
$
f = {\mu _S}N \\
\Rightarrow {\mu _S} = \dfrac{f}{N} \\
$
Using this in equation (iii), we get
$
\dfrac{{{v^2}}}{{Rg}} = \dfrac{{\sin \theta + {\mu _S}\cos \theta }}{{\cos \theta - {\mu _S}\sin \theta }} \\
\Rightarrow v = \sqrt {Rg\left( {\dfrac{{\sin \theta + {\mu _S}\cos \theta }}{{\cos \theta - {\mu _S}\sin \theta }}} \right)} \\
$
This is the required expression for the velocity of the car. Hence, the correct answer is option B.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: It should be noted that we have written the second equation on the basis of the fact that the horizontal component of the normal reaction force provides the necessary centripetal force required to move the car on the curved turn of the road. While moving on the curved road, the car requires a centripetal force to move in a curve.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




