
A body thrown vertically up to reach its maximum height in $t$ second. The total time from the time of projection to reach a point at half of its maximum height while returning (in second) in
A) $\sqrt 2 t$
B) $1 + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}t$
C) $\dfrac{3}{2}t$
D) $\dfrac{t}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: The time taken to reach maximum height is equal to the time taken to reach to the earth as drag due to air is not considered while solving the projectile equations. Also, the horizontal acceleration is zero the only acceleration is in a vertical direction and which is the acceleration due to gravity. The acceleration for vertical motion will be acceleration due to gravity with a proper sign which is decided by the direction of motion of the body.
Formula used:
The formula of the Newton’s law of motion is $v = u + at$ and ${v^2} = {u^2} + 2as$ where $v$ is the final velocity, $u$ is initial velocity, $a$ is acceleration, $t$ is time and s is displacement.
Complete step by step answer:
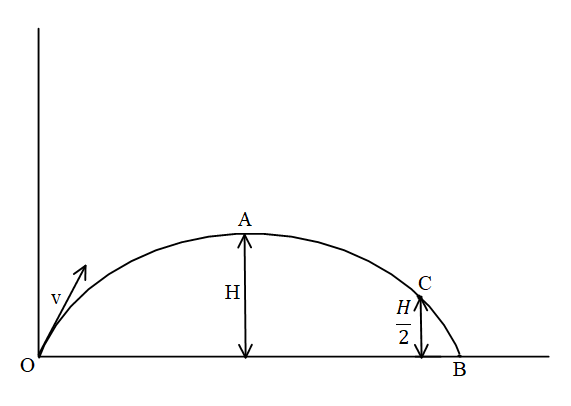
For the vertical motion, the time taken to reach maximum height is $H$ is,
${v_A}^2 = {v_o}^2 - 2gH$
As the final velocity is zero at maximum height.
$\Rightarrow 0 = {v_o}^2 - 2gH$
$\Rightarrow {v_o} = \sqrt {2gH} $………eq. (1)
$\Rightarrow {v_A} = {v_o} + at$
$\Rightarrow 0 = {v_o} - gt$
$\Rightarrow t = \dfrac{{{v_o}}}{g}$………eq. (2)
Replace the value of ${v_o}$ from equation (1) to equation (2).
$ t = \dfrac{{{v_o}}}{g}$
$\Rightarrow t = \dfrac{{\sqrt {2gH} }}{g}$
$\Rightarrow t = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2H}}{g}} $………eq. (3)
Applying the relation for the motion from the point A and C.
$ {v^2} = {u^2} + 2as$
$\Rightarrow {v_C}^2 = {v_A}^2 + 2as$
$\Rightarrow {v_C}^2 = 0 + 2g\left( {\dfrac{H}{2}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {v_C}^2 = 0 + gH$
$\Rightarrow {v_C} = \sqrt {gH} $………………….…eq. (4)
For the motion from A to C.
${v_C} = {v_A} + a{t_1}$
$\Rightarrow {v_C} = 0 + g{t_1}$
$\Rightarrow {v_C} = g{t_1}$…………………...……eq. (5)
Replace the value of ${v_C}$ from the equation (5).
$\Rightarrow {v_C} = g{t_1}$
$\Rightarrow \sqrt {gH} = g{t_1}$
\[\Rightarrow {t_1} = \sqrt {\dfrac{H}{g}} \]………………………...eq. (6)
Comparing equation (1) and (6).
\[ {t_1} = \dfrac{t}{{\sqrt 2 }}\]……………...……eq. (7)
So the time taken to half of the maximum height while returning is equal to,
$\Rightarrow {t_2} = t + {t_1}$
$\Rightarrow {t_2} = t + \dfrac{t}{{\sqrt 2 }}$ (Replace the value of ${t_1}$from equation (7))
$\Rightarrow {t_2} = t\left( {1 + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)$
Hence the correct answer is option B.
Note:
The sign of acceleration due to gravity is positive only if the motion is in the direction of acceleration due to gravity and the sign is negative if the motion is in the opposite direction of acceleration due to gravity.
Formula used:
The formula of the Newton’s law of motion is $v = u + at$ and ${v^2} = {u^2} + 2as$ where $v$ is the final velocity, $u$ is initial velocity, $a$ is acceleration, $t$ is time and s is displacement.
Complete step by step answer:

For the vertical motion, the time taken to reach maximum height is $H$ is,
${v_A}^2 = {v_o}^2 - 2gH$
As the final velocity is zero at maximum height.
$\Rightarrow 0 = {v_o}^2 - 2gH$
$\Rightarrow {v_o} = \sqrt {2gH} $………eq. (1)
$\Rightarrow {v_A} = {v_o} + at$
$\Rightarrow 0 = {v_o} - gt$
$\Rightarrow t = \dfrac{{{v_o}}}{g}$………eq. (2)
Replace the value of ${v_o}$ from equation (1) to equation (2).
$ t = \dfrac{{{v_o}}}{g}$
$\Rightarrow t = \dfrac{{\sqrt {2gH} }}{g}$
$\Rightarrow t = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2H}}{g}} $………eq. (3)
Applying the relation for the motion from the point A and C.
$ {v^2} = {u^2} + 2as$
$\Rightarrow {v_C}^2 = {v_A}^2 + 2as$
$\Rightarrow {v_C}^2 = 0 + 2g\left( {\dfrac{H}{2}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {v_C}^2 = 0 + gH$
$\Rightarrow {v_C} = \sqrt {gH} $………………….…eq. (4)
For the motion from A to C.
${v_C} = {v_A} + a{t_1}$
$\Rightarrow {v_C} = 0 + g{t_1}$
$\Rightarrow {v_C} = g{t_1}$…………………...……eq. (5)
Replace the value of ${v_C}$ from the equation (5).
$\Rightarrow {v_C} = g{t_1}$
$\Rightarrow \sqrt {gH} = g{t_1}$
\[\Rightarrow {t_1} = \sqrt {\dfrac{H}{g}} \]………………………...eq. (6)
Comparing equation (1) and (6).
\[ {t_1} = \dfrac{t}{{\sqrt 2 }}\]……………...……eq. (7)
So the time taken to half of the maximum height while returning is equal to,
$\Rightarrow {t_2} = t + {t_1}$
$\Rightarrow {t_2} = t + \dfrac{t}{{\sqrt 2 }}$ (Replace the value of ${t_1}$from equation (7))
$\Rightarrow {t_2} = t\left( {1 + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)$
Hence the correct answer is option B.
Note:
The sign of acceleration due to gravity is positive only if the motion is in the direction of acceleration due to gravity and the sign is negative if the motion is in the opposite direction of acceleration due to gravity.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE

Why was the Vernacular Press Act passed by British class 11 social science CBSE




