
A body of mass ‘m’ is suspended to an ideal spring of spring constant ‘k’. The expected change in position of a body due to an additional force ‘F’ acting vertically downwards is –
\[\begin{align}
& \text{A) }\dfrac{3F}{2k} \\
& \text{B) }\dfrac{2F}{k} \\
& \text{C) }\dfrac{5F}{2k} \\
& \text{D) }\dfrac{4F}{k} \\
\end{align}\]
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: We are given a spring and mass system with the physical quantities related to them. We can easily find the displacement of the spring from the mean position due to mass and the given additional force using the energy stored in the spring system.
Complete answer:
We are given an ideal spring which has an initial mass hung on it as we can see in the below figure. According to Hooke's law, the force acting on the spring due to the mass is proportional to the displacement made by the spring from its mean position.
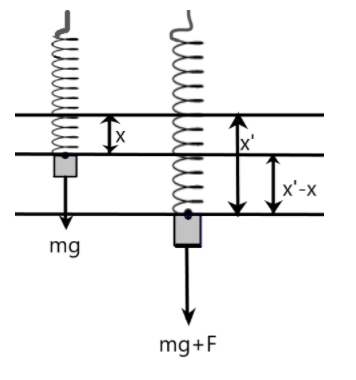
The work done by the mass on the spring against gravity is stored as the energy in the spring. We can equate these energies as –
\[\begin{align}
& \text{Work done by mass against gravity, W}=\text{ Energy stored in the spring, E} \\
& \Rightarrow {{W}_{g}}={{E}_{s}} \\
& \Rightarrow mgx=\dfrac{1}{2}k{{x}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{2mg}{k}\text{ --(1)} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let us consider the second situation in which an additional force ‘F’ is applied on the system. The work done by the mass ‘m’ and the additional force ‘F’ is stored as energy in the spring. Here, more energy is stored in the system, therefore, the elongation of the spring will be longer which can be given as –
\[\begin{align}
& {{W}_{g}}+F={{E}_{s}} \\
& \Rightarrow (mg+F)x'=\dfrac{1}{2}kx{{'}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow x'=\dfrac{2mg+2F}{k}\text{ --(2)} \\
\end{align}\]
So, we have the elongation due to the two different situations in (1) and (2). We can find the difference between these two elongations to find the effect of the additional force on the spring as –
\[\begin{align}
& \text{The change in elongation, }\delta =x'-x \\
& \Rightarrow \delta =\dfrac{2mg+2F}{k}-\dfrac{2mg}{k} \\
& \therefore \delta =\dfrac{2F}{k} \\
\end{align}\]
The extra elongation of the spring due to the additional force F is \[\dfrac{2F}{k}\].
The correct answer is option B.
Note:
We should be considering the energy stored in the system while finding the elongation of the spring instead of directly applying the Hooke’s law because the force doesn’t give a complete account on the displacement which we require as the elongation.
Complete answer:
We are given an ideal spring which has an initial mass hung on it as we can see in the below figure. According to Hooke's law, the force acting on the spring due to the mass is proportional to the displacement made by the spring from its mean position.

The work done by the mass on the spring against gravity is stored as the energy in the spring. We can equate these energies as –
\[\begin{align}
& \text{Work done by mass against gravity, W}=\text{ Energy stored in the spring, E} \\
& \Rightarrow {{W}_{g}}={{E}_{s}} \\
& \Rightarrow mgx=\dfrac{1}{2}k{{x}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{2mg}{k}\text{ --(1)} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let us consider the second situation in which an additional force ‘F’ is applied on the system. The work done by the mass ‘m’ and the additional force ‘F’ is stored as energy in the spring. Here, more energy is stored in the system, therefore, the elongation of the spring will be longer which can be given as –
\[\begin{align}
& {{W}_{g}}+F={{E}_{s}} \\
& \Rightarrow (mg+F)x'=\dfrac{1}{2}kx{{'}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow x'=\dfrac{2mg+2F}{k}\text{ --(2)} \\
\end{align}\]
So, we have the elongation due to the two different situations in (1) and (2). We can find the difference between these two elongations to find the effect of the additional force on the spring as –
\[\begin{align}
& \text{The change in elongation, }\delta =x'-x \\
& \Rightarrow \delta =\dfrac{2mg+2F}{k}-\dfrac{2mg}{k} \\
& \therefore \delta =\dfrac{2F}{k} \\
\end{align}\]
The extra elongation of the spring due to the additional force F is \[\dfrac{2F}{k}\].
The correct answer is option B.
Note:
We should be considering the energy stored in the system while finding the elongation of the spring instead of directly applying the Hooke’s law because the force doesn’t give a complete account on the displacement which we require as the elongation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




