
A block of mass m=1 Kg is at rest on a rough horizontal surface having coefficient of static friction ${\mu _s} = 0.2$ and kinetic force ${\mu _k} = 0.15$. Discuss the frictional force if a horizontal force F is applied on the block.
Sr. No. Value of F 1. 1N 2. 2N 3. 2.5N
| Sr. No. | Value of F |
| 1. | 1N |
| 2. | 2N |
| 3. | 2.5N |

Answer
591k+ views
Hint: A body will move only if the external force applied on it overcomes the force exerted by static friction. Once in motion, the kinetic friction will exert force in the direction opposite to the motion of the body with respect to the ground.
Formula Used:
1. Force due to gravity \[{F_g} = mg\] ……(1)
Where,
m is the mass of the object
g is the acceleration due to gravity (10m/s2)
2. Maximum friction force exerted by the rough surface: \[{f_{\max }} = {\mu _s}N\] ……(2)
This is the force a body needs to overcome to attain the state of motion.
Where,
\[{\mu _s}\] is the coefficient of static friction
N is the normal force acting on the body.
3. Kinetic friction force exerted by the rough surface: \[f = {\mu _k}N\] ……(3)
Where,
\[{\mu _k}\] is the coefficient of kinetic friction
Complete step by step answer:
Diagram:
Free body diagram of the block.
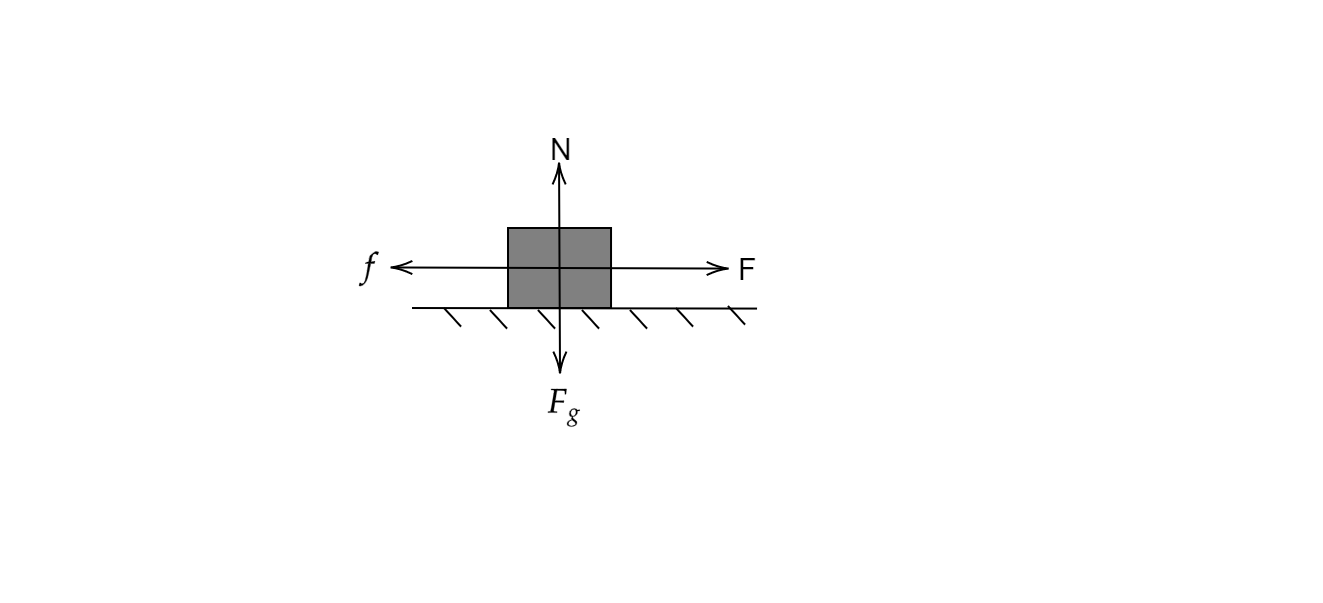
Given:
1. Mass of the object m=1kg
2. Coefficient of static friction ${\mu _s} = 0.2$
3. Coefficient of kinetic force ${\mu _k} = 0.15$
To find: The nature of frictional force in each case.
Step1:
Calculate the force on the body due to gravity using eq (1):
\[
\Rightarrow {F_g} = 1 \times 10 \\
\Rightarrow {F_g} = 10N \\
\]
As there is no force in acceleration of the body in the vertical direction: \[{F_g} = N\]. So, \[N = 10N\].
Step 2:
Find the maximum force exerted by the rough surface on the block using eq (2):
\[
\Rightarrow {f_{\max }} = 0.2 \times 10 \\
\Rightarrow {f_{\max }} = 2N \\
\]
Case 1:
F applied towards the right is less than the limiting friction or maximum friction applied by the rough surface towards the left: \[{f_{\max }} > F\]
This implies that the body will remain in rest. For a body in rest, the forces towards right and left cancel out:
\[
\Rightarrow f = F \\
\Rightarrow f = 1N \\
\]
Case 2:
F applied towards the right is just equal to the limiting friction or maximum friction applied by the rough surface towards the left: \[{f_{\max }} = F\]
This implies that the body is just on the verge to change its state to motion but till the force exerts this limiting force it will remain in rest. For a body in rest, the forces towards right and left cancel out:
\[
\Rightarrow f = F \\
\Rightarrow f = 2N \\
\]
Case 3:
F applied towards the right is greater than the limiting friction or maximum friction applied by the rough surface towards the left: \[{f_{\max }} < F\]
This implies that the body is now in motion. For a body in motion, kinetic friction acts on it to resist its motion in the direction opposite to the motion. Find the force exerted due to kinetic friction using eq (3):
\[
\Rightarrow f = 0.15 \times 1 \\
\Rightarrow f = 0.15N \\
\]
Note: Remember that for a body at rest, the net force acting on it is 0. So, if a body on a rough surface is at rest even after a force is acting on it, then the friction force of the same magnitude must be acting on it in the opposite direction.
Formula Used:
1. Force due to gravity \[{F_g} = mg\] ……(1)
Where,
m is the mass of the object
g is the acceleration due to gravity (10m/s2)
2. Maximum friction force exerted by the rough surface: \[{f_{\max }} = {\mu _s}N\] ……(2)
This is the force a body needs to overcome to attain the state of motion.
Where,
\[{\mu _s}\] is the coefficient of static friction
N is the normal force acting on the body.
3. Kinetic friction force exerted by the rough surface: \[f = {\mu _k}N\] ……(3)
Where,
\[{\mu _k}\] is the coefficient of kinetic friction
Complete step by step answer:
Diagram:
Free body diagram of the block.

Given:
1. Mass of the object m=1kg
2. Coefficient of static friction ${\mu _s} = 0.2$
3. Coefficient of kinetic force ${\mu _k} = 0.15$
To find: The nature of frictional force in each case.
Step1:
Calculate the force on the body due to gravity using eq (1):
\[
\Rightarrow {F_g} = 1 \times 10 \\
\Rightarrow {F_g} = 10N \\
\]
As there is no force in acceleration of the body in the vertical direction: \[{F_g} = N\]. So, \[N = 10N\].
Step 2:
Find the maximum force exerted by the rough surface on the block using eq (2):
\[
\Rightarrow {f_{\max }} = 0.2 \times 10 \\
\Rightarrow {f_{\max }} = 2N \\
\]
Case 1:
F applied towards the right is less than the limiting friction or maximum friction applied by the rough surface towards the left: \[{f_{\max }} > F\]
This implies that the body will remain in rest. For a body in rest, the forces towards right and left cancel out:
\[
\Rightarrow f = F \\
\Rightarrow f = 1N \\
\]
Case 2:
F applied towards the right is just equal to the limiting friction or maximum friction applied by the rough surface towards the left: \[{f_{\max }} = F\]
This implies that the body is just on the verge to change its state to motion but till the force exerts this limiting force it will remain in rest. For a body in rest, the forces towards right and left cancel out:
\[
\Rightarrow f = F \\
\Rightarrow f = 2N \\
\]
Case 3:
F applied towards the right is greater than the limiting friction or maximum friction applied by the rough surface towards the left: \[{f_{\max }} < F\]
This implies that the body is now in motion. For a body in motion, kinetic friction acts on it to resist its motion in the direction opposite to the motion. Find the force exerted due to kinetic friction using eq (3):
\[
\Rightarrow f = 0.15 \times 1 \\
\Rightarrow f = 0.15N \\
\]
Note: Remember that for a body at rest, the net force acting on it is 0. So, if a body on a rough surface is at rest even after a force is acting on it, then the friction force of the same magnitude must be acting on it in the opposite direction.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




