
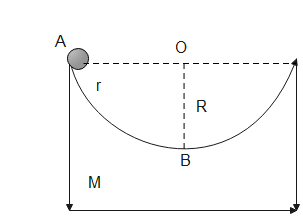
A block of mass M with a semi circular track of radius R, rests on a horizontal frictionless surface. A uniform cylinder of radius r and mass m is released from rest at the top point A. The cylinder slips on the semicircular frictionless track. How far has the block moved when the cylinder reaches the bottom of the track? How fast is the block moving when the cylinder reaches the bottom of the track?

Answer
572.4k+ views
Hint: To solve this question we use the concept of center of mass. That block which shows in the left is named as m. First we have to find the center of mass and origin through considering block m move x left and cylinder of mass m moves (R−r−x) right side of the semicircular track.
Complete Step by step solution:
According to the concept of center of mass. We consider block m moves x left and cylinder of mass m move (R−r−x) right side we write.
$\begin{array}{l}
{X_{Com}} = \dfrac{{m\left( {R - r - x} \right) - xM}}{{m + M}}\\
\Rightarrow {X_{Com}} = m\left( {R - r} \right) - mx - xM = 0\\
x = \dfrac{{m\left( {R - r} \right)}}{{\left( {M + m} \right)}}
\end{array}$
Therefore we have a center of mass and origin.
$\begin{array}{l}
\sqrt {2{K_M}M} = \sqrt {2{K_m}m} \\
\therefore \dfrac{{{K_M}}}{{{K_m}}} = \dfrac{m}{M} - - - - - - (1)\\
2{K_m} = mg\left( {R - r} \right) - - - - - - (2)
\end{array}$
Solving these two equation
$\dfrac{1}{2}M{v_M}^2$
$\therefore {v_M} = m\sqrt {\dfrac{{2g\left( {R - r} \right)}}{{M\left( {M + m} \right)}}} $
Hence we get speed of the block moving when the cylinder reaches the bottom of the track.
Additional information:
$\bullet$ Here the interesting thing about the center of mass of an object is that it is the point where any uniform force on the object acts. This is very useful for solving mechanics problems where we have to describe the motion of oddly-shaped objects and complicated systems like in this problem.
$\bullet$ Centre of mass of a body is nothing but what we defined as a point at which the whole of the mass of the body or all the masses of a system of particles appears to be concentrated.
$\bullet$ Benefit of using the center of mass in physics to model a mass distribution can be seen by considering the resultant of the gravity forces on a continuous body.
Note:
We can consider the center of mass of a uniform disc shape would be at its center. Because the center of mass is a position defined as a system of objects. So, it is the average position of all the parts of the system, weighted according to their masses. Center of mass is also called the center of gravity and the center of mass of an object is a position vector.
Complete Step by step solution:
According to the concept of center of mass. We consider block m moves x left and cylinder of mass m move (R−r−x) right side we write.
$\begin{array}{l}
{X_{Com}} = \dfrac{{m\left( {R - r - x} \right) - xM}}{{m + M}}\\
\Rightarrow {X_{Com}} = m\left( {R - r} \right) - mx - xM = 0\\
x = \dfrac{{m\left( {R - r} \right)}}{{\left( {M + m} \right)}}
\end{array}$
Therefore we have a center of mass and origin.
$\begin{array}{l}
\sqrt {2{K_M}M} = \sqrt {2{K_m}m} \\
\therefore \dfrac{{{K_M}}}{{{K_m}}} = \dfrac{m}{M} - - - - - - (1)\\
2{K_m} = mg\left( {R - r} \right) - - - - - - (2)
\end{array}$
Solving these two equation
$\dfrac{1}{2}M{v_M}^2$
$\therefore {v_M} = m\sqrt {\dfrac{{2g\left( {R - r} \right)}}{{M\left( {M + m} \right)}}} $
Hence we get speed of the block moving when the cylinder reaches the bottom of the track.
Additional information:
$\bullet$ Here the interesting thing about the center of mass of an object is that it is the point where any uniform force on the object acts. This is very useful for solving mechanics problems where we have to describe the motion of oddly-shaped objects and complicated systems like in this problem.
$\bullet$ Centre of mass of a body is nothing but what we defined as a point at which the whole of the mass of the body or all the masses of a system of particles appears to be concentrated.
$\bullet$ Benefit of using the center of mass in physics to model a mass distribution can be seen by considering the resultant of the gravity forces on a continuous body.
Note:
We can consider the center of mass of a uniform disc shape would be at its center. Because the center of mass is a position defined as a system of objects. So, it is the average position of all the parts of the system, weighted according to their masses. Center of mass is also called the center of gravity and the center of mass of an object is a position vector.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




