
A bicycle is resting on its stand in the east - west direction and the rear wheel is rotating at 100 revolutions per minute. Length of each spoke is 30 cm, and the vertical component of the earth’s magnetism is $1.5\times {{10}^{-5}}$ tesla. If the emf induced in the spoke is $3\pi \times {{10}^{-6}}V$, then the angle of dip is:
A. ${{\tan }^{-1}}(\dfrac{3}{4})$
B. ${{\tan }^{-1}}(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}})$
C. ${{\tan }^{-1}}(\sqrt{3})$
D. ${{\tan }^{-1}}(\dfrac{1}{3})$
Answer
588.3k+ views
Hint: The number of magnetic field lines moving through a given closed surface is known as magnetic flux. The calculation of the total magnetic field which passes through a given surface area is provided. The bicycle rests in the east-west direction, so horizontal magnetic field lines of the magnetization of the earth will be cut across the wheel spokes. This question can easily be solved using the formula for the Induced emf.
Formula Used: For solving this question, we will be using the formula for the Induced emf, i.e.,
\[emf=\dfrac{d\phi }{dt}\]
Complete step-by-step solution
Before we start solving the question that is given to us, let us take a look at all the parameters that are given to us in the above question
Radius of the spoke = r = 30 cm
Area covered in one revolution = \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\]
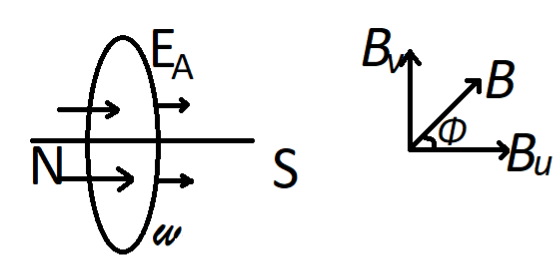
Induced emf = \[3\pi \times {{10}^{-6}}V\]
Earth’s magnetism = $1.5\times {{10}^{-5}}$ tesla
Flux is magnetic field times the area covered in unit time because the magnetic field (B) is constant.
So,
Area covered in one revolution = \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\]
Area covered in one second = \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\times \dfrac{100}{60}\]
Therefore,
We have the equation for the emf
$\Rightarrow \pi {{r}^{2}}\times \dfrac{100}{60}\times B=3\pi \times {{10}^{-6}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{9}{100}\times \dfrac{100}{60}\times B=3\times {{10}^{-6}}$
$\Rightarrow B=3\times {{10}^{-6}}\times \dfrac{100}{9}\times \dfrac{60}{100}$
$\Rightarrow B=2\times {{10}^{-5}}Tesla$
Now,
As the vertical field = $1.5\times {{10}^{-5}}$ tesla
So,
Angle of dip = ${{\tan }^{-1}}(\dfrac{1.5\times {{10}^{-5}}}{2\times {{10}^{-5}}})$
$\Rightarrow Angle\text{ }of\text{ }dip\text{ }={{\tan }^{-1}}(\dfrac{3}{4})$
So,
The angle of dip is ${{\tan }^{-1}}(\dfrac{3}{4})$, i.e., Option-A
Note: The angle made in the magnetic meridian between the sum of the magnetic field of the earth and the surface of the earth (horizontal component) is referred to as the dip angle. For field maps and geological fields, the dip angle plays a significant role. The dip assists in ensuring the steepest angle of descent relative to a horizontal plane for every tilted bed.
Formula Used: For solving this question, we will be using the formula for the Induced emf, i.e.,
\[emf=\dfrac{d\phi }{dt}\]
Complete step-by-step solution
Before we start solving the question that is given to us, let us take a look at all the parameters that are given to us in the above question
Radius of the spoke = r = 30 cm
Area covered in one revolution = \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\]
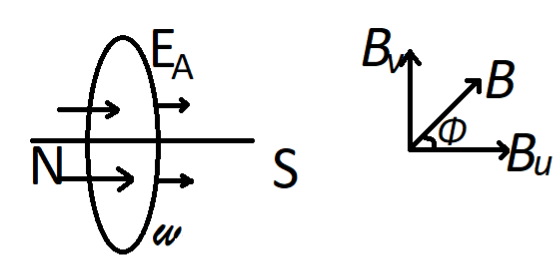
Induced emf = \[3\pi \times {{10}^{-6}}V\]
Earth’s magnetism = $1.5\times {{10}^{-5}}$ tesla
Flux is magnetic field times the area covered in unit time because the magnetic field (B) is constant.
So,
Area covered in one revolution = \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\]
Area covered in one second = \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\times \dfrac{100}{60}\]
Therefore,
We have the equation for the emf
$\Rightarrow \pi {{r}^{2}}\times \dfrac{100}{60}\times B=3\pi \times {{10}^{-6}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{9}{100}\times \dfrac{100}{60}\times B=3\times {{10}^{-6}}$
$\Rightarrow B=3\times {{10}^{-6}}\times \dfrac{100}{9}\times \dfrac{60}{100}$
$\Rightarrow B=2\times {{10}^{-5}}Tesla$
Now,
As the vertical field = $1.5\times {{10}^{-5}}$ tesla
So,
Angle of dip = ${{\tan }^{-1}}(\dfrac{1.5\times {{10}^{-5}}}{2\times {{10}^{-5}}})$
$\Rightarrow Angle\text{ }of\text{ }dip\text{ }={{\tan }^{-1}}(\dfrac{3}{4})$
So,
The angle of dip is ${{\tan }^{-1}}(\dfrac{3}{4})$, i.e., Option-A
Note: The angle made in the magnetic meridian between the sum of the magnetic field of the earth and the surface of the earth (horizontal component) is referred to as the dip angle. For field maps and geological fields, the dip angle plays a significant role. The dip assists in ensuring the steepest angle of descent relative to a horizontal plane for every tilted bed.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




