
A ball of mass m and radius r rolls along a circular path of radius R. Its speed at the bottom ($\theta ={{0}^{{}^\circ }}$) of the path is ${{v}_{0}}$. Find the force of the path on the ball as a function of $\theta$

Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: We should know that velocity is defined as the rate change of displacement per unit time. Speed in a specific direction is also known as velocity. Velocity is equal to displacement divided by time. Speed, being a scalar quantity, is the rate at which an object covers distance. The average speed is the distance which is a scalar quantity per time ratio. On the other hand, velocity is a vector quantity; it is direction-aware. An object which moves in the negative direction has a negative velocity. If the object is slowing down then its acceleration vector is directed in the opposite direction as its motion in this case. Based on this we have to solve this question.
Complete step by step answer
Let us consider the diagram that is given below:
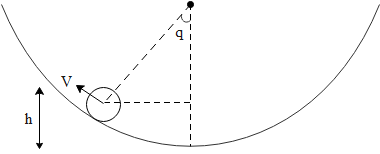
Let us derive the first equation as:
$\mathrm{h}=(\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{r})(1-\cos \theta) \ldots. .(\mathrm{i})$
Kinetic energy at angle $\theta$ is given as: $\mathrm{K}=\dfrac{7}{5}\left(\dfrac{1}{2} \mathrm{mv}_{0}^{2}\right)-\mathrm{mgh}$
In case of pure rolling we can write that: $\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{T}}=\dfrac{5}{7} \mathrm{k}$
Therefore, the relation that is developed is given below:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} \mathrm{mv}^{2}=\dfrac{1}{2} \mathrm{mv}_{0}^{2}-\dfrac{5}{7} \mathrm{mgh}$
Now we can write the second expression as:
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{v}^{2}=\mathrm{v}_{0}^{2}-\dfrac{10}{7} \mathrm{gh} \ldots$(ii)
Equation of motion at angle $\theta$ is given as: $\mathrm{n}-\mathrm{mg} \cos \theta=\dfrac{\mathrm{mv}^{2}}{(\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{r})}$
Now we can write that:
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{N}=\mathrm{mg} \cos \theta+\dfrac{\mathrm{m}}{(\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{r})}\left(\mathrm{v}_{0}^{2}-\dfrac{10}{7} \mathrm{gh}\right)$
Substituting value of $h$ from Eq. (i) to get:
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{N}=\mathrm{mg} \cos \theta+\left(\dfrac{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{r}}\right)$
So, the expression can be written as: $\left\{\mathrm{v}_{0}^{2}-\dfrac{10}{7} \mathrm{g}(\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{r})(1-\cos \theta)\right\}$
On further evaluation we get:
$=\dfrac{\mathrm{mg}}{7}(17 \cos \theta-10)+\dfrac{\mathrm{mv}_{0}^{2}}{(\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{r})}$
Force of friction is given as:
$\mathrm{f}=\dfrac{\mathrm{mg} \sin \theta}{1+\dfrac{\mathrm{m} \mathrm{m}^{2}}{\mathrm{I}}}$ (for pure rolling to take place this is the condition)
On further evaluation we get:
$=\dfrac{\operatorname{mg} \sin \theta}{1+\dfrac{5}{2}}\left(\mathrm{I}=\dfrac{2}{5} \mathrm{mr}^{2}\right)$
So, we get the result as:
$=\dfrac{2}{7} \mathrm{mg} \sin \theta$
Hence the force of the path of the bath in the function of $\theta$is given as: $\dfrac{2}{7}mg\sin \theta$.
Note: We should know that if an object's speed or velocity is increasing at a constant rate then we say it has uniform acceleration. The rate of acceleration is constant. If a car speeds up then slows down then speeds up it doesn't have uniform acceleration. The instantaneous acceleration, or simply acceleration, is defined as the limit of the average acceleration when the interval of time considered approaches 0. It is also defined in a similar manner as the derivative of velocity with respect to time. If an object begins acceleration from rest or a standstill, its initial time is 0. If we get a negative value for acceleration, it means the object is slowing down. The acceleration of an object is its change in velocity over an increment of time. This can mean a change in the object's speed or direction. Average acceleration is the change of velocity over a period of time. Constant or uniform acceleration is when the velocity changes the same amount in every equal time period.
Complete step by step answer
Let us consider the diagram that is given below:

Let us derive the first equation as:
$\mathrm{h}=(\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{r})(1-\cos \theta) \ldots. .(\mathrm{i})$
Kinetic energy at angle $\theta$ is given as: $\mathrm{K}=\dfrac{7}{5}\left(\dfrac{1}{2} \mathrm{mv}_{0}^{2}\right)-\mathrm{mgh}$
In case of pure rolling we can write that: $\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{T}}=\dfrac{5}{7} \mathrm{k}$
Therefore, the relation that is developed is given below:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} \mathrm{mv}^{2}=\dfrac{1}{2} \mathrm{mv}_{0}^{2}-\dfrac{5}{7} \mathrm{mgh}$
Now we can write the second expression as:
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{v}^{2}=\mathrm{v}_{0}^{2}-\dfrac{10}{7} \mathrm{gh} \ldots$(ii)
Equation of motion at angle $\theta$ is given as: $\mathrm{n}-\mathrm{mg} \cos \theta=\dfrac{\mathrm{mv}^{2}}{(\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{r})}$
Now we can write that:
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{N}=\mathrm{mg} \cos \theta+\dfrac{\mathrm{m}}{(\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{r})}\left(\mathrm{v}_{0}^{2}-\dfrac{10}{7} \mathrm{gh}\right)$
Substituting value of $h$ from Eq. (i) to get:
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{N}=\mathrm{mg} \cos \theta+\left(\dfrac{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{r}}\right)$
So, the expression can be written as: $\left\{\mathrm{v}_{0}^{2}-\dfrac{10}{7} \mathrm{g}(\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{r})(1-\cos \theta)\right\}$
On further evaluation we get:
$=\dfrac{\mathrm{mg}}{7}(17 \cos \theta-10)+\dfrac{\mathrm{mv}_{0}^{2}}{(\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{r})}$
Force of friction is given as:
$\mathrm{f}=\dfrac{\mathrm{mg} \sin \theta}{1+\dfrac{\mathrm{m} \mathrm{m}^{2}}{\mathrm{I}}}$ (for pure rolling to take place this is the condition)
On further evaluation we get:
$=\dfrac{\operatorname{mg} \sin \theta}{1+\dfrac{5}{2}}\left(\mathrm{I}=\dfrac{2}{5} \mathrm{mr}^{2}\right)$
So, we get the result as:
$=\dfrac{2}{7} \mathrm{mg} \sin \theta$
Hence the force of the path of the bath in the function of $\theta$is given as: $\dfrac{2}{7}mg\sin \theta$.
Note: We should know that if an object's speed or velocity is increasing at a constant rate then we say it has uniform acceleration. The rate of acceleration is constant. If a car speeds up then slows down then speeds up it doesn't have uniform acceleration. The instantaneous acceleration, or simply acceleration, is defined as the limit of the average acceleration when the interval of time considered approaches 0. It is also defined in a similar manner as the derivative of velocity with respect to time. If an object begins acceleration from rest or a standstill, its initial time is 0. If we get a negative value for acceleration, it means the object is slowing down. The acceleration of an object is its change in velocity over an increment of time. This can mean a change in the object's speed or direction. Average acceleration is the change of velocity over a period of time. Constant or uniform acceleration is when the velocity changes the same amount in every equal time period.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




