
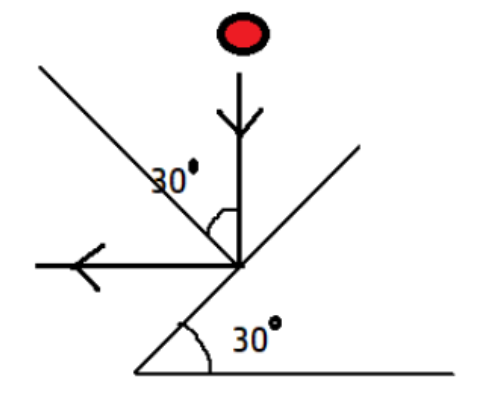
A ball is released from a point, it goes vertically downwards and collides with a fixed smooth inclined plane of angle of inclination of 30 \[{}^\circ \]from the restitution between the ball and the inclined plane is
(A) \[\dfrac{1}{2}\]
(B) \[\dfrac{1}{3}\]
(C) 1
(D) none of these

Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint:A ball collides with an inclined plane of inclination \[30{}^\circ \] after falling through a distance, since it moves horizontally just after the impact. We can use here the concept of coefficient of restitution to arrive at the solution.
Complete step by step answer:
A ball is just dropped say from a height h,
To find the velocity at the impact using the third equation of motion we get,
\[\begin{align}
& {{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}=2gh \\
&\therefore v=\sqrt{2gh} \\
\end{align}\]
Now let us resolve the velocity vector,
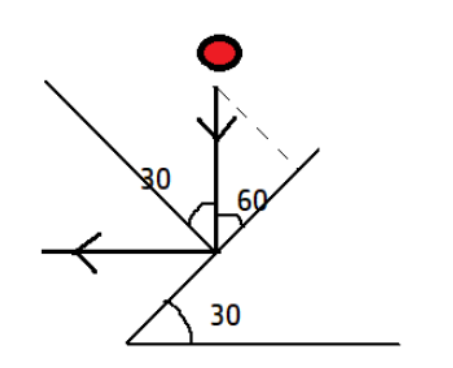
Component of velocity parallel to the plane is \[v\cos 60\]= \[\dfrac{v}{2}\]
Component of velocity perpendicular to the plane is \[v\sin 60=\dfrac{v\sqrt{3}}{2}\]
From the figure, it is clear that velocity parallel to the plane remains the same since the rebound velocity is horizontal,
Coefficient of restitution, e= \[\dfrac{{{v}_{2}}}{{{v}_{1}}}=\dfrac{v\cos 60}{v\cos 30}=\dfrac{1}{3}\]
So the value of e comes out to be \[\dfrac{1}{3}\]. Hence, the correct option is (B).
Additional Information:
The coefficient of restitution denoted by (e) is the ratio of the final to initial relative velocity. It indicates how much kinetic energy remains after a collision between two bodies. It normally ranges from 0 to 1 where 1 would be a perfectly elastic collision. For a perfectly elastic collision, it would mean the final and initial velocities are the same and that means the complete transfer of energy but that is an ideal case.
Note: Here we have resolved the velocities because the ball after being dropped is striking an inclined plane which is inclined at a given angle. We must be careful while resolving the given vector. The initial velocity is taken zero because the ball was dropped.
Complete step by step answer:
A ball is just dropped say from a height h,
To find the velocity at the impact using the third equation of motion we get,
\[\begin{align}
& {{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}=2gh \\
&\therefore v=\sqrt{2gh} \\
\end{align}\]
Now let us resolve the velocity vector,

Component of velocity parallel to the plane is \[v\cos 60\]= \[\dfrac{v}{2}\]
Component of velocity perpendicular to the plane is \[v\sin 60=\dfrac{v\sqrt{3}}{2}\]
From the figure, it is clear that velocity parallel to the plane remains the same since the rebound velocity is horizontal,
Coefficient of restitution, e= \[\dfrac{{{v}_{2}}}{{{v}_{1}}}=\dfrac{v\cos 60}{v\cos 30}=\dfrac{1}{3}\]
So the value of e comes out to be \[\dfrac{1}{3}\]. Hence, the correct option is (B).
Additional Information:
The coefficient of restitution denoted by (e) is the ratio of the final to initial relative velocity. It indicates how much kinetic energy remains after a collision between two bodies. It normally ranges from 0 to 1 where 1 would be a perfectly elastic collision. For a perfectly elastic collision, it would mean the final and initial velocities are the same and that means the complete transfer of energy but that is an ideal case.
Note: Here we have resolved the velocities because the ball after being dropped is striking an inclined plane which is inclined at a given angle. We must be careful while resolving the given vector. The initial velocity is taken zero because the ball was dropped.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




