
A ball is dropped from a height of 20m above the surface of a water in a lake. The refractive index of water is 4/3. A fish inside the lake, in the line of fall of the ball, is looking at the ball. At an instant when the ball is 12.8m above the water surface, the fish sees the speed of the ball as-
a)9m/s
b)12m/s
c)16m/s
d)21.33m/s
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: We are asked basically to calculate the speed of the ball observed by the fish at instant when the ball is 12.8m above the surface of the lake. At every position of the ball with respect to the surface of the lake at any instant time, the fish will observe the ball to be at greater height than its actual height. Hence we will obtain the equation of the position of the ball with respect to the position of fish inside water and accordingly differentiate the equation to obtain the velocity of the ball observed by the fish.
Formula used:
$D=x+\mu h$
${{V}^{2}}-{{U}^{2}}=2gs$
Complete answer:
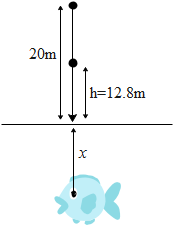
To begin with let us first determine the speed of the ball when it is above 12.8m from the surface of the water. Let us say a body free falls due to gravity where acceleration due to gravity is $g=10m{{s}^{-2}}$. Let the initial speed of the body be ‘U’. Then when it covers a distance of s meters than the velocity of the body at that point ‘V’ is given by,
${{V}^{2}}-{{U}^{2}}=2gs$
When the ball moves from 20 m to 12.8m above the surface of water, the distance covered by the ball is
$s=20-12.8=7.2m$. Hence from above equation the velocity of the ball at that point is,
$\begin{align}
& {{V}^{2}}-{{U}^{2}}=2gs \\
& \Rightarrow {{V}^{2}}-0=2\times 10\times 7.2 \\
& \Rightarrow V=\sqrt{144}m{{s}^{-1}}=12m{{s}^{-1}} \\
\end{align}$
Let us say the fish is at a distance x from the surface of the water. Hence the fish will see the ball slightly raised from the actual position of the ball. Let us say the actual position of the ball from the surface of the water is h and the refractive index of water is ($\mu $). Then the distance D from the fish to the apparent position of the ball is equal to,
$D=x+\mu h$
Differentiating this equation we get with respect to time we get
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{dD}{dt}=\dfrac{dx}{dt}+\mu \dfrac{dh}{dt}\text{, }\because \dfrac{dx}{dt}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dD}{dt}=\dfrac{4}{3}12m{{s}^{-1}}=16m{{s}^{-1}} \\
\end{align}$
Hence the fish will observe the ball to have a velocity of 16 meter per second when it is 12.89m from the surface of the lake.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
In the above solution we have considered $\dfrac{dx}{dt}=0$ as the fish does not move with time. If the fish moves as well the velocity of the ball observed at the same instant of time will be different. It will be either greater or smaller than the above velocity seen depending on the relative motion between the two.
Formula used:
$D=x+\mu h$
${{V}^{2}}-{{U}^{2}}=2gs$
Complete answer:

To begin with let us first determine the speed of the ball when it is above 12.8m from the surface of the water. Let us say a body free falls due to gravity where acceleration due to gravity is $g=10m{{s}^{-2}}$. Let the initial speed of the body be ‘U’. Then when it covers a distance of s meters than the velocity of the body at that point ‘V’ is given by,
${{V}^{2}}-{{U}^{2}}=2gs$
When the ball moves from 20 m to 12.8m above the surface of water, the distance covered by the ball is
$s=20-12.8=7.2m$. Hence from above equation the velocity of the ball at that point is,
$\begin{align}
& {{V}^{2}}-{{U}^{2}}=2gs \\
& \Rightarrow {{V}^{2}}-0=2\times 10\times 7.2 \\
& \Rightarrow V=\sqrt{144}m{{s}^{-1}}=12m{{s}^{-1}} \\
\end{align}$
Let us say the fish is at a distance x from the surface of the water. Hence the fish will see the ball slightly raised from the actual position of the ball. Let us say the actual position of the ball from the surface of the water is h and the refractive index of water is ($\mu $). Then the distance D from the fish to the apparent position of the ball is equal to,
$D=x+\mu h$
Differentiating this equation we get with respect to time we get
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{dD}{dt}=\dfrac{dx}{dt}+\mu \dfrac{dh}{dt}\text{, }\because \dfrac{dx}{dt}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dD}{dt}=\dfrac{4}{3}12m{{s}^{-1}}=16m{{s}^{-1}} \\
\end{align}$
Hence the fish will observe the ball to have a velocity of 16 meter per second when it is 12.89m from the surface of the lake.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
In the above solution we have considered $\dfrac{dx}{dt}=0$ as the fish does not move with time. If the fish moves as well the velocity of the ball observed at the same instant of time will be different. It will be either greater or smaller than the above velocity seen depending on the relative motion between the two.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




