
A ball falls from height $h$. After $1\,s$, another ball falls freely from a point $25\,m$ below the point from when the first ball falls. Both of them reach the ground at the same time. The value of $h$ is
$A.\,{\text{ 1}}1.2{\text{ }}m$
$B.\,{\text{ 2}}1.2{\text{ }}m$
$C.\,{\text{ }}31.2{\text{ }}m$
$D.\,{\text{ 4}}1.2{\text{ }}m$
Answer
515.7k+ views
Hint: In order to solve the question, we will use the Newton’s second law of motion on both the ball on ball A we will use it to find the time of flight of ball A while that time of flight will be use to substitute while calculating the value of h by applying the formula on ball B hence we will get to the answer
Formula used:
Newton’s second law of motion
$s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
Here, $s$ refers to displacement, $u$ refers to initial velocity, $a$ refers to acceleration and $t$ refers to time period.
Complete step by step answer:
In the question we are given A ball falls from height h. After 1s, another ball falls freely from a point 25m below the point from when the first ball falls. Both of then reach the ground at the same time and we have to find the value of $h$ is
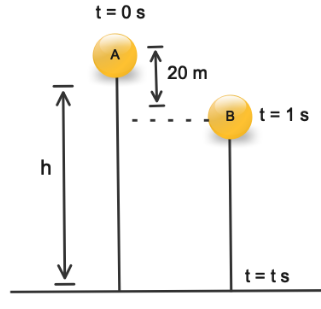
Let us take the time of flight of ball A = t s
Then, the time of flight of ball B = (t – 1) s
Now by applying Newton's second law we will find the value of $h$.
For Ball A: By using ball A we will find the time of flight of it.
Distance travelled = h
Time taken to travel distance = t s
Initial velocity = 0
Acceleration applied = g
Now applying the formula
$s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
Substituting the value
$h = 0(t) + \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$
Solving the equation for t
$t = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2h}}{g}} {\text{ }}s$
For Ball B: By using time of flight of ball A we will find the value of $h$.
Distance travelled = (h-20)
Time taken to travel distance = (t -1) s
Initial velocity = 0
Acceleration applied = g
Now applying the formula
$s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
Substituting the value
$(h - 20) = 0(t - 1) + \dfrac{1}{2}g{(t - 1)^2}$
Solving the equation for h
$(h - 20) = \dfrac{1}{2}g{(t - 1)^2}$
Opening the square of time period
$h - 20 = \dfrac{{g{t^2}}}{2} + \dfrac{g}{2} - gt$
Substituting the time of flight of ball, A $t = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2h}}{g}} {\text{ }}s$
$h - 20 = \dfrac{g}{2}\left( {\dfrac{{2h}}{g}} \right) + \dfrac{g}{2} - g\sqrt {\dfrac{{2h}}{g}} $
$\Rightarrow h - 20 = h + \dfrac{g}{2} - g\sqrt {\dfrac{{2h}}{g}} $
h on both side will cut off
$h = \dfrac{{{{\left( {\dfrac{g}{2} + 20} \right)}^2}}}{{2g}}$
Now taking the value of $g = 10{\text{ m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}$
$h = \dfrac{{{{\left( {\dfrac{{10}}{2} + 20} \right)}^2}}}{{2 \times 10}}$
$\Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{{{\left( {25} \right)}^2}}}{{20}}$
$\therefore h = 31.25{\text{ }}m$
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note: Many of the students will make the mistake while calculation in ball b for finding h by substituting the value of t before opening the bracket of time of flight but first of fall we will open the bracket of time of flight then we have to substitute the value of t and value of g is taken $10{\text{ }}m{s^{ - 2}}$ instead of ${\text{9}}{\text{.8 }}m{s^{ - 2}}$ so as to make calculation easy as well as to match to the options.
Formula used:
Newton’s second law of motion
$s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
Here, $s$ refers to displacement, $u$ refers to initial velocity, $a$ refers to acceleration and $t$ refers to time period.
Complete step by step answer:
In the question we are given A ball falls from height h. After 1s, another ball falls freely from a point 25m below the point from when the first ball falls. Both of then reach the ground at the same time and we have to find the value of $h$ is

Let us take the time of flight of ball A = t s
Then, the time of flight of ball B = (t – 1) s
Now by applying Newton's second law we will find the value of $h$.
For Ball A: By using ball A we will find the time of flight of it.
Distance travelled = h
Time taken to travel distance = t s
Initial velocity = 0
Acceleration applied = g
Now applying the formula
$s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
Substituting the value
$h = 0(t) + \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$
Solving the equation for t
$t = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2h}}{g}} {\text{ }}s$
For Ball B: By using time of flight of ball A we will find the value of $h$.
Distance travelled = (h-20)
Time taken to travel distance = (t -1) s
Initial velocity = 0
Acceleration applied = g
Now applying the formula
$s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
Substituting the value
$(h - 20) = 0(t - 1) + \dfrac{1}{2}g{(t - 1)^2}$
Solving the equation for h
$(h - 20) = \dfrac{1}{2}g{(t - 1)^2}$
Opening the square of time period
$h - 20 = \dfrac{{g{t^2}}}{2} + \dfrac{g}{2} - gt$
Substituting the time of flight of ball, A $t = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2h}}{g}} {\text{ }}s$
$h - 20 = \dfrac{g}{2}\left( {\dfrac{{2h}}{g}} \right) + \dfrac{g}{2} - g\sqrt {\dfrac{{2h}}{g}} $
$\Rightarrow h - 20 = h + \dfrac{g}{2} - g\sqrt {\dfrac{{2h}}{g}} $
h on both side will cut off
$h = \dfrac{{{{\left( {\dfrac{g}{2} + 20} \right)}^2}}}{{2g}}$
Now taking the value of $g = 10{\text{ m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}$
$h = \dfrac{{{{\left( {\dfrac{{10}}{2} + 20} \right)}^2}}}{{2 \times 10}}$
$\Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{{{\left( {25} \right)}^2}}}{{20}}$
$\therefore h = 31.25{\text{ }}m$
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note: Many of the students will make the mistake while calculation in ball b for finding h by substituting the value of t before opening the bracket of time of flight but first of fall we will open the bracket of time of flight then we have to substitute the value of t and value of g is taken $10{\text{ }}m{s^{ - 2}}$ instead of ${\text{9}}{\text{.8 }}m{s^{ - 2}}$ so as to make calculation easy as well as to match to the options.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




