
5 beats/ second are heard when a tuning fork is sounded with a sonometer wire under tension, when the length of the sonometer wire is either 0.95m or 1m. The frequency of the fork will be:
A. \[\;195Hz\]
B. \[251{\text{ }}Hz\]
C. \[150Hz\]
D. \[300Hz\]
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: By assuming the length of the wire, we will be able to figure out its wavelength. Once it is known, we can determine the frequency of the sonometer wire. By substituting this wavelength value in velocity, frequency and wavelength equation, we can find the frequency of the wire for its two different lengths. Finally, using the beat equation for both the frequencies, the frequency of the tuning fork is found out.
Formula used:
Velocity, frequency and wavelength relation: $\lambda = \dfrac{v}{f}$
Where $f$ is the frequency of the wire and is expressed in Hertz $(Hz)$, $v$ is the velocity of the vibrating wire and is expressed in meter per second $(m/s)$ and $\lambda $ is the wavelength of the wire and is expressed in meter $(m)$.
Beat equation: $\left| {f - F} \right|$
Where $F$ is the frequency of the tuning fork and is expressed in Hertz $(Hz)$.
Complete step by step answer:
The constitution of a wavelength is one crest and one trough.
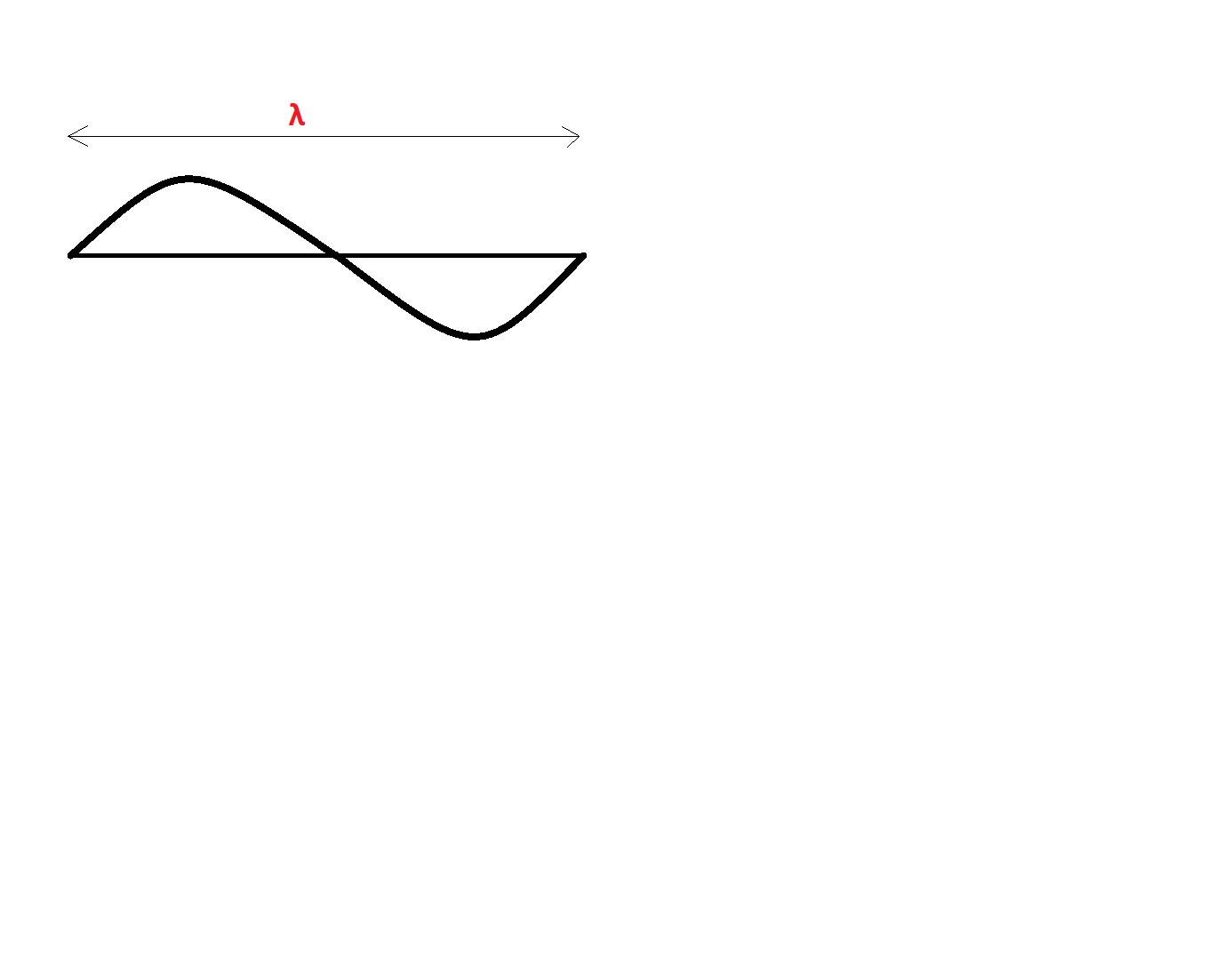
But in our wire, the wave is incomplete. That is, over a length of, suppose $l$, the wavelength is $\lambda /2$.
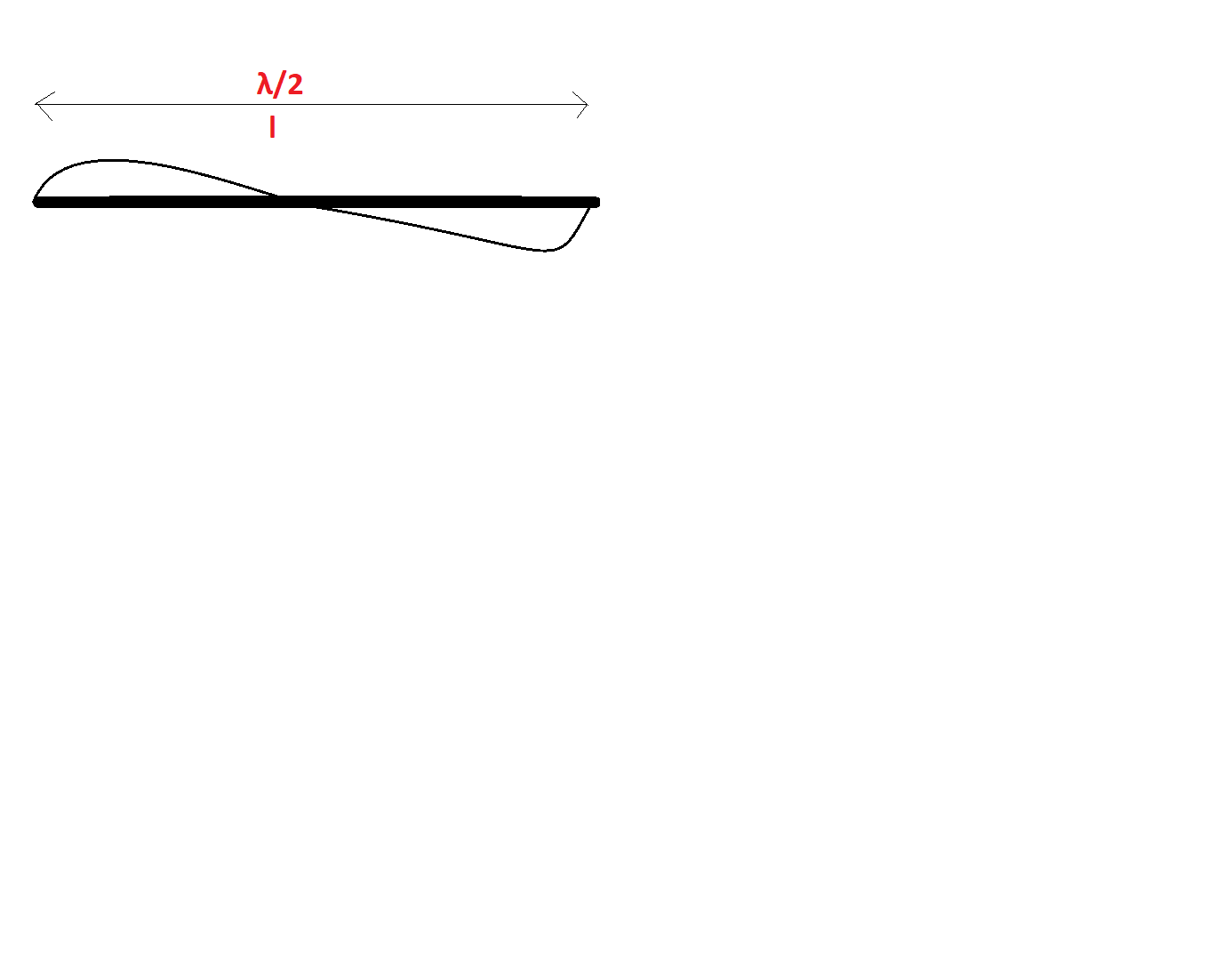
Therefore, $\lambda = 2l$.
Using this in velocity, frequency and wavelength relation we get,
$\lambda = \dfrac{v}{f} \\
\Rightarrow f = \dfrac{v}{\lambda } = \dfrac{v}{{2l}} \\
\Rightarrow f = \dfrac{v}{{2l}} \\
$
We are given two values of length of the wire. Let's call it${l_1} = 0.95m$ and ${l_2} = 1m$.
Substituting these values of lengths we will find two values of frequency ${f_{1,}}{f_2}$.
Therefore,
$
{f_1} = \dfrac{v}{{2{l_1}}} = \dfrac{v}{{2 \times 0.95}} \\
\Rightarrow {f_1} = \dfrac{v}{{1.9}} \\
$
and,
$
{f_2} = \dfrac{v}{{2{l_2}}} = \dfrac{v}{{2 \times 1}} \\
\Rightarrow {f_2} = \dfrac{v}{2} \\
$
Now to find the frequency of the tuning fork we will use the beat equation $\left| {f - F} \right|$. We know the beat number as well.
For ${f_{1,}}{f_2}$ value we will establish two different equations.
Therefore,
$
5 = \left| {{f_1} - F} \right| \\
5 = \left| {{f_2} - F} \right| \\
$
Substituting the frequency values we get,
$
5 = \left| {{f_1} - F} \right| \Rightarrow 5 = \left| {\dfrac{v}{{1.9}} - F} \right| \\
5 = \left| {{f_2} - F} \right| \Rightarrow 5 = \left| {\dfrac{v}{2} - F} \right| \\
$
When we solve these two simultaneously we get,
$F = 195Hz$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
The frequency of the fork should not be confused with the frequency of the fork. Only bet formula includes frequency of fork. Whereas, velocity, wavelength, frequency relation uses frequency of the wire.
Formula used:
Velocity, frequency and wavelength relation: $\lambda = \dfrac{v}{f}$
Where $f$ is the frequency of the wire and is expressed in Hertz $(Hz)$, $v$ is the velocity of the vibrating wire and is expressed in meter per second $(m/s)$ and $\lambda $ is the wavelength of the wire and is expressed in meter $(m)$.
Beat equation: $\left| {f - F} \right|$
Where $F$ is the frequency of the tuning fork and is expressed in Hertz $(Hz)$.
Complete step by step answer:
The constitution of a wavelength is one crest and one trough.

But in our wire, the wave is incomplete. That is, over a length of, suppose $l$, the wavelength is $\lambda /2$.

Therefore, $\lambda = 2l$.
Using this in velocity, frequency and wavelength relation we get,
$\lambda = \dfrac{v}{f} \\
\Rightarrow f = \dfrac{v}{\lambda } = \dfrac{v}{{2l}} \\
\Rightarrow f = \dfrac{v}{{2l}} \\
$
We are given two values of length of the wire. Let's call it${l_1} = 0.95m$ and ${l_2} = 1m$.
Substituting these values of lengths we will find two values of frequency ${f_{1,}}{f_2}$.
Therefore,
$
{f_1} = \dfrac{v}{{2{l_1}}} = \dfrac{v}{{2 \times 0.95}} \\
\Rightarrow {f_1} = \dfrac{v}{{1.9}} \\
$
and,
$
{f_2} = \dfrac{v}{{2{l_2}}} = \dfrac{v}{{2 \times 1}} \\
\Rightarrow {f_2} = \dfrac{v}{2} \\
$
Now to find the frequency of the tuning fork we will use the beat equation $\left| {f - F} \right|$. We know the beat number as well.
For ${f_{1,}}{f_2}$ value we will establish two different equations.
Therefore,
$
5 = \left| {{f_1} - F} \right| \\
5 = \left| {{f_2} - F} \right| \\
$
Substituting the frequency values we get,
$
5 = \left| {{f_1} - F} \right| \Rightarrow 5 = \left| {\dfrac{v}{{1.9}} - F} \right| \\
5 = \left| {{f_2} - F} \right| \Rightarrow 5 = \left| {\dfrac{v}{2} - F} \right| \\
$
When we solve these two simultaneously we get,
$F = 195Hz$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
The frequency of the fork should not be confused with the frequency of the fork. Only bet formula includes frequency of fork. Whereas, velocity, wavelength, frequency relation uses frequency of the wire.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




