
When $2 - $heptyne was treated with aqueous sulphuric acid containing mercury$(II)$sulphate, two products, each having the molecular formula ${C_7}{H_{14}}O$, were obtained in approximately equal amount. What are these two compounds$?$
$A)$$3 - $heptanone
$B)$heptan$3,4$dione
$C)$$2 - $heptanone
$D)$heptan$3,4$diol
Answer
517.8k+ views
Hint: This is an oxymercuration reaction. Oxymercuration is not limited to an alkene reacting with water. Using an alkyne instead of an alkene yields an enol, which tautomerizes into a ketone. Using alcohol instead of water yields an ether. In both cases, Markovnikov's rule is observed.
Complete answer:
Oxymercuration involves mercury acting as a reagent attacking the alkene double bond to form a mercurinium ion bridge. A water molecule will then attack the most substituted carbon to open the mercurium ion bridge, followed by proton transfer to solvent water molecule.
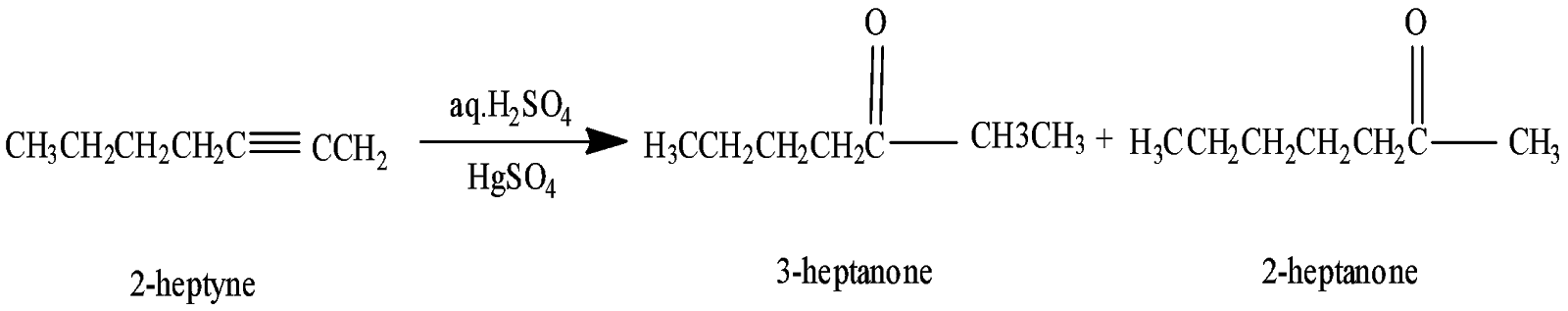
When $2 - $heptyne was treated with aqueous sulphuric acid containing mercury$(II)$ sulphate it gives $3 - heptanone$ and $2 - heptanone$.
Oxymercuration is very regioselective and is a Markovnikov reaction ruling out extreme cases, the water nucleophile will always preferentially attack the more substituted carbon, depositing the resultant hydroxy group there.
$HgS{O_4}$ adds first, in an anti-Markovnikov fashion, forcing a $H$ from ${H_3}{O^ + }$ to add on the terminal carbon and thus water to add to the other side. ${H_2}S{O_4}$ makes the formation of ${H_3}{O^ + }$ more favorable.
So the correct answer is $A)$$3 - $heptanone and $C)$$2 - $heptanone.
Note:
During the oxymercuration reaction the mercury adduct product is almost always treated with sodium borohydride in aqueous base in a reaction called demercuration. In demercuration, the acetyl mercury group is replaced with a hydrogen in a stereochemically insensitive reaction known as reductive elimination.
Complete answer:
Oxymercuration involves mercury acting as a reagent attacking the alkene double bond to form a mercurinium ion bridge. A water molecule will then attack the most substituted carbon to open the mercurium ion bridge, followed by proton transfer to solvent water molecule.

When $2 - $heptyne was treated with aqueous sulphuric acid containing mercury$(II)$ sulphate it gives $3 - heptanone$ and $2 - heptanone$.
Oxymercuration is very regioselective and is a Markovnikov reaction ruling out extreme cases, the water nucleophile will always preferentially attack the more substituted carbon, depositing the resultant hydroxy group there.
$HgS{O_4}$ adds first, in an anti-Markovnikov fashion, forcing a $H$ from ${H_3}{O^ + }$ to add on the terminal carbon and thus water to add to the other side. ${H_2}S{O_4}$ makes the formation of ${H_3}{O^ + }$ more favorable.
So the correct answer is $A)$$3 - $heptanone and $C)$$2 - $heptanone.
Note:
During the oxymercuration reaction the mercury adduct product is almost always treated with sodium borohydride in aqueous base in a reaction called demercuration. In demercuration, the acetyl mercury group is replaced with a hydrogen in a stereochemically insensitive reaction known as reductive elimination.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE




