
2, 4-Dinitrochlorobenzene is less reactive than chlorobenzene towards nucleophilic substitution. (State whether the given statements are True or False).
A. True
B. False
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint:Nucleophilic substitution reactions are those reactions in which an electron rich nucleophile tends to attack a positively charged electrophile in order to replace a leaving group.
Complete answer:
The structures of 2, 4-Dinitrochlorobenzene and chlorobenzene are displayed below:
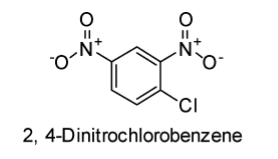
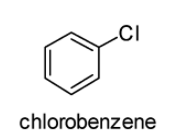
In case of chlorobenzene, the lone pair of electrons are delocalised on the benzene ring. Therefore, \[C - Cl\] bond tends to acquire the slight partial double bond character. As a result, \[C - Cl\] bond in the chlorobenzene molecule is very strong which cannot be broken easily.
In case of the 2, 4-Dinitrochlorobenzene, nitro-group (\[N{O_2}\]) is present, which is an electron-withdrawing group. Thus, presence of \[N{O_2}\] group at the para position tends to withdraw the electrons from the benzene ring and thereby facilitates the attack of nucleophiles on the para chlorobenzene. Hence, para nitrochlorobenzene seems to be more reactive towards the nucleophilic substitution reactions in comparison to chlorobenzene.
Therefore, the given statement i.e. 2, 4-Dinitrochlorobenzene is less reactive than chlorobenzene towards nucleophilic substitution, cannot be true.
Hence, the correct answer is Option B i.e. false.
Note:
In simpler terms, nucleophilic substitution reactions are those reactions in which an electron pair donor (i.e. a nucleophile say ‘Y’:) reacts with an electron pair acceptor (i.e. a substrate, say ‘R-X’) and which substitutes for the ‘X’ group (i.e. a leaving group). Let us look at the following generalized equation for nucleophilic substitution:
$Y{:^ - } + R - X \to Y - R + :{X^ - }$
Here, $R$ can be an alkyl or an aryl group.
Complete answer:
The structures of 2, 4-Dinitrochlorobenzene and chlorobenzene are displayed below:


In case of chlorobenzene, the lone pair of electrons are delocalised on the benzene ring. Therefore, \[C - Cl\] bond tends to acquire the slight partial double bond character. As a result, \[C - Cl\] bond in the chlorobenzene molecule is very strong which cannot be broken easily.
In case of the 2, 4-Dinitrochlorobenzene, nitro-group (\[N{O_2}\]) is present, which is an electron-withdrawing group. Thus, presence of \[N{O_2}\] group at the para position tends to withdraw the electrons from the benzene ring and thereby facilitates the attack of nucleophiles on the para chlorobenzene. Hence, para nitrochlorobenzene seems to be more reactive towards the nucleophilic substitution reactions in comparison to chlorobenzene.
Therefore, the given statement i.e. 2, 4-Dinitrochlorobenzene is less reactive than chlorobenzene towards nucleophilic substitution, cannot be true.
Hence, the correct answer is Option B i.e. false.
Note:
In simpler terms, nucleophilic substitution reactions are those reactions in which an electron pair donor (i.e. a nucleophile say ‘Y’:) reacts with an electron pair acceptor (i.e. a substrate, say ‘R-X’) and which substitutes for the ‘X’ group (i.e. a leaving group). Let us look at the following generalized equation for nucleophilic substitution:
$Y{:^ - } + R - X \to Y - R + :{X^ - }$
Here, $R$ can be an alkyl or an aryl group.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




