
2, 3 dimethyl but-2-ene when reacted with bromine forms a compound which upon heating with alcoholic $ \text{KOH} $ produces the following major product:
(A)
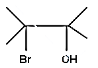
(B)
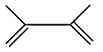
(C)
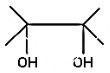
(D)
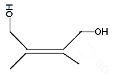




Answer
556.5k+ views
Hint: The addition of alcoholic $ \text{KOH} $ to an alkyl halide followed by heating the substance leads to the formation of an alkene and this takes place through an elimination reaction. The hydroxyl atom of the alcohol acts as a string base that helps in the extraction of a beta hydrogen atom from the alkyl halide.
Complete Stepwise Solution:
The reaction of 2, 2 dimethyl but-2-ene with bromine can be given as follows:
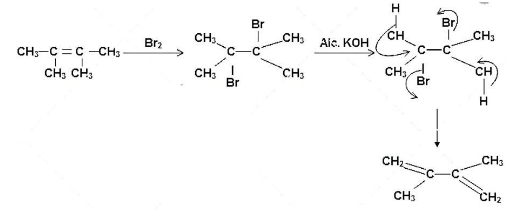
In the first step, the bromine molecule adds onto the carbon atoms of the double bond to form 2,3 – dibromo, 2,3-dimethyl butane. The addition of the alcoholic potassium hydroxide solution follows next that results in the formation of the 2,3-dimethyl but-1, 3- dinene. This is from the attack of the hydroxyl group of alcoholic potassium hydroxide that attacks the beta-hydrogen atoms with respect to the bromine atoms and two beta-elimination reactions take place in the molecule leading to the formation of the diene.
Hence, the compound formed when 2, 3 dimethyl but-2-ene reacts with bromine forms a compound which upon heating with alcoholic $ \text{KOH} $ is 2,3-dimethyl but-1, 3- dinene, option B.
Note:
The bromination of the alkenes or the alkynes is a non-stereoselective reaction as the bromine molecule being non-polar, it adds onto the alkene or the alkyne non-selectively. Potassium hydroxide when dissolved in water and that aqueous solution is added to any alkene or alkyne then it behaves as a strong base that adds to the double bond and forms the alcohol from the alkene and alkynes.
Complete Stepwise Solution:
The reaction of 2, 2 dimethyl but-2-ene with bromine can be given as follows:

In the first step, the bromine molecule adds onto the carbon atoms of the double bond to form 2,3 – dibromo, 2,3-dimethyl butane. The addition of the alcoholic potassium hydroxide solution follows next that results in the formation of the 2,3-dimethyl but-1, 3- dinene. This is from the attack of the hydroxyl group of alcoholic potassium hydroxide that attacks the beta-hydrogen atoms with respect to the bromine atoms and two beta-elimination reactions take place in the molecule leading to the formation of the diene.
Hence, the compound formed when 2, 3 dimethyl but-2-ene reacts with bromine forms a compound which upon heating with alcoholic $ \text{KOH} $ is 2,3-dimethyl but-1, 3- dinene, option B.
Note:
The bromination of the alkenes or the alkynes is a non-stereoselective reaction as the bromine molecule being non-polar, it adds onto the alkene or the alkyne non-selectively. Potassium hydroxide when dissolved in water and that aqueous solution is added to any alkene or alkyne then it behaves as a strong base that adds to the double bond and forms the alcohol from the alkene and alkynes.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




