
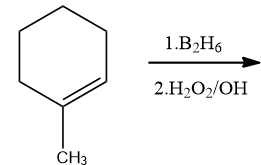
1-Methylcyclohexene is allowed to react with ${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$. The product is then treated with ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ and NaOH. The product formed is:

Answer
593.4k+ views
Hint: Hydration reaction of alkene can take place using acid-catalysed reaction, and hydroboration oxidation. Acid-catalysed reaction proceeds through Markovnikov’s rule and Hydroboration oxidation proceeds through anti-markovnikov’s rule.
Complete step by step answer: This is a reaction of alkene with ${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ followed with hydrogen peroxide and Base. This reaction is an example of Hydroboration oxidation. Hydroboration oxidation reaction is a two step hydration reaction that converts alkene into an alcohol. The process results in the syn-addition of a hydrogen and a hydroxyl group where the double bond had been. The reaction proceeded through anti-markovnikov’s rule. The OH group is added to that carbon which has more hydrogen, and hydrogen is added to that carbon which has more hydrogen.
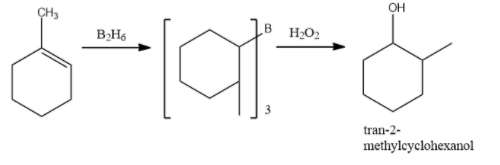
In the first step, Borane($B{{H}_{3}}$) adds to the double bond, transferring one of the hydrogen atoms to the carbon adjacent to the one that becomes bonded to the boron. The hydroboration is repeated two additional times, successively reacting each B-H bond so that three alkenes add to each $B{{H}_{3}}$. The resulting trialkylborane is treated with hydrogen peroxide in the second step. This process replaces the B-C bonds with OH-C bonds. The boron reagent is converted to boric acid.
Note: Hydroboration proceeds in an anti markovnikov manner. The reaction sequence is also stereospecific, giving syn addition, the hydroboration syn-selective and the oxidation replaces the boron with hydroxyl having the same geometric position.
Complete step by step answer: This is a reaction of alkene with ${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ followed with hydrogen peroxide and Base. This reaction is an example of Hydroboration oxidation. Hydroboration oxidation reaction is a two step hydration reaction that converts alkene into an alcohol. The process results in the syn-addition of a hydrogen and a hydroxyl group where the double bond had been. The reaction proceeded through anti-markovnikov’s rule. The OH group is added to that carbon which has more hydrogen, and hydrogen is added to that carbon which has more hydrogen.

In the first step, Borane($B{{H}_{3}}$) adds to the double bond, transferring one of the hydrogen atoms to the carbon adjacent to the one that becomes bonded to the boron. The hydroboration is repeated two additional times, successively reacting each B-H bond so that three alkenes add to each $B{{H}_{3}}$. The resulting trialkylborane is treated with hydrogen peroxide in the second step. This process replaces the B-C bonds with OH-C bonds. The boron reagent is converted to boric acid.
Note: Hydroboration proceeds in an anti markovnikov manner. The reaction sequence is also stereospecific, giving syn addition, the hydroboration syn-selective and the oxidation replaces the boron with hydroxyl having the same geometric position.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




