
(1) Refer to the Fischer projection formula of ribose. Furanose form of ribose is produced by the addition of –OH group at C-4 to aldehyde. Draw Haworth projection formula of four stereoisomeric ribofuranose using D, L and $\alpha ,\beta $notations.
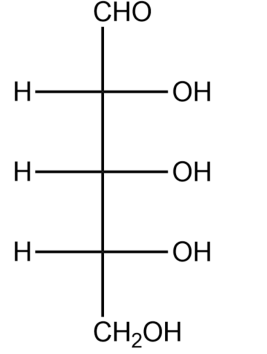
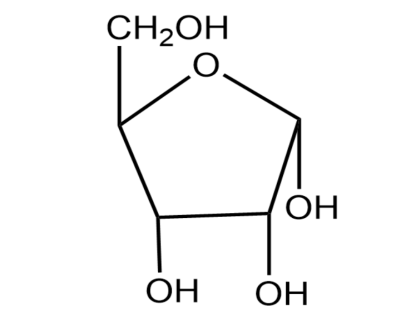
(2) Adjacent is the Haworth projection formula of $\alpha -D$ ribulofuranose. Write its Fischer projection formula.


Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: Furanose is a collective term for carbohydrates that represents a chemical structure including a five-membered ring system consisting of four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. Chemically furanose is a cyclic hemiacetal of an aldopentose or a cyclic hemiketal of a ketohexose.
Complete answer:
-Furanose ring consists of four carbon and one oxygen atom having an anomeric carbon to the right of the oxygen atom. The highest numbered chiral carbon determines whether the structure will have D-configuration or L-configuration.
-Furanose with an L-configuration has the substituent on the highest numbered chiral carbon which is pointed downwards out of the plane and in a D-structure furanose, the highest-numbered chiral carbon is facing upwards.
-Depending on the direction of anomeric hydroxyl group pointing, the furanose ring will either have alpha or beta configuration. In a D-configuration of furanose, if the hydroxyl group is pointing down then it is an alpha configuration and if the hydroxyl group pointing up then it is a beta configuration. Similarly, it is opposite with respect to an L-configuration.
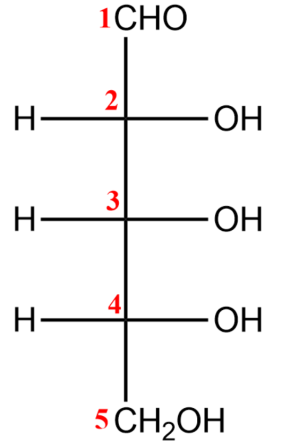
-For converting a Fisher projection to a Haworth projection, we will follow the following steps-
(i) You first need to number carbons and draw in the Fisher stereochemistry.
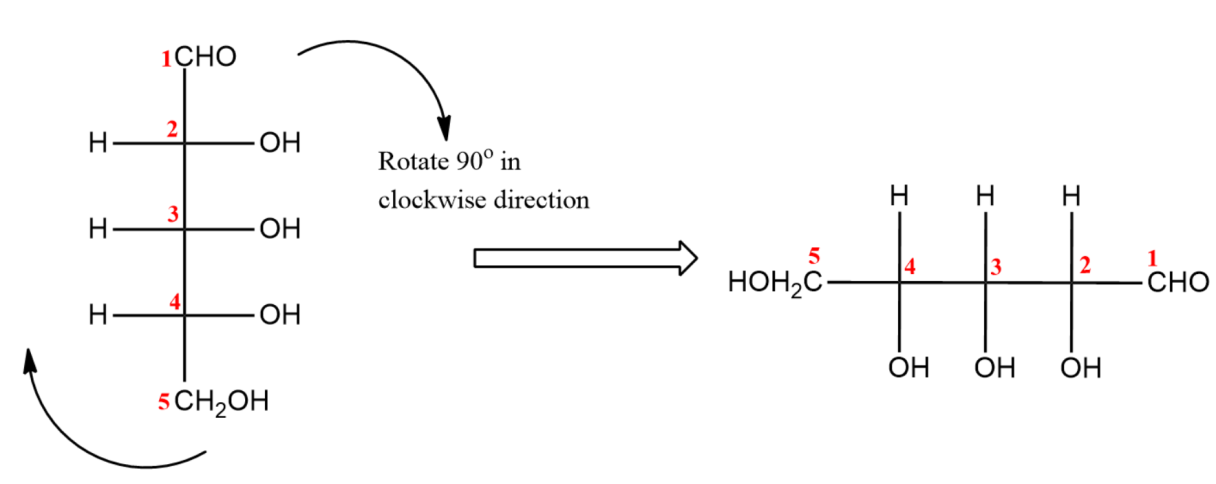
(ii) Now, rotate the molecule to $90{}^\circ $ in clockwise direction.
(iii) Next step is the bond rotation of ${{C}_{4}}$with ${{C}_{5}}$.
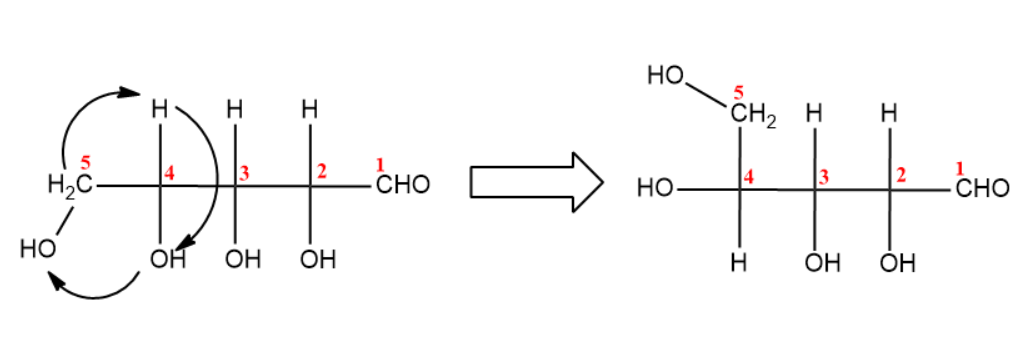
(iv) Last step is the closure of fischer projection forming a closed ring structure.
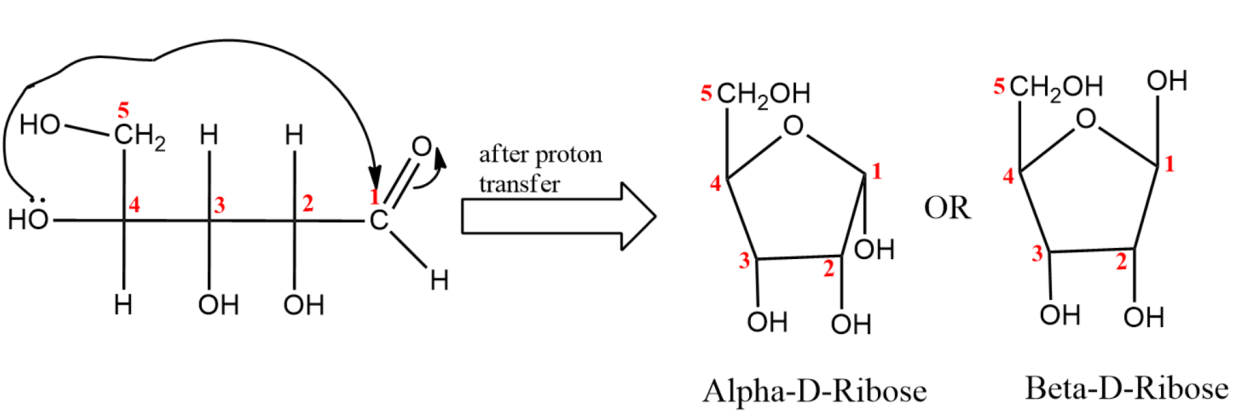
(2) In the next part of the question, we are asked to write Fisher projection of $\alpha -D$Ribulofuranose.
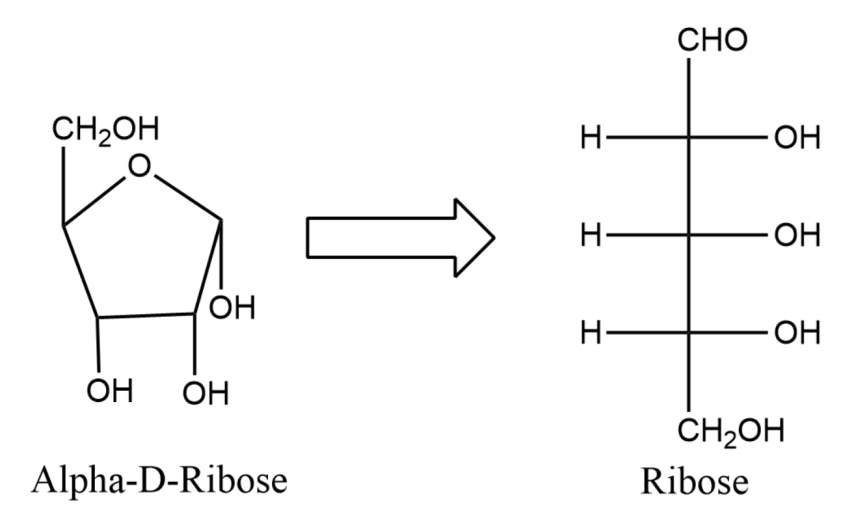
Note:
For D-sugars, the last carbon will end up at the top of the Haworth projection. For L-sugars, the last carbon will end up on the top of the Haworth projection. At ${{C}_{1}}$ for D-sugars, if the OH group is down then it is an alpha-anomer whereas if the OH group is up then it is a beta-anomer.
Complete answer:
-Furanose ring consists of four carbon and one oxygen atom having an anomeric carbon to the right of the oxygen atom. The highest numbered chiral carbon determines whether the structure will have D-configuration or L-configuration.
-Furanose with an L-configuration has the substituent on the highest numbered chiral carbon which is pointed downwards out of the plane and in a D-structure furanose, the highest-numbered chiral carbon is facing upwards.
-Depending on the direction of anomeric hydroxyl group pointing, the furanose ring will either have alpha or beta configuration. In a D-configuration of furanose, if the hydroxyl group is pointing down then it is an alpha configuration and if the hydroxyl group pointing up then it is a beta configuration. Similarly, it is opposite with respect to an L-configuration.
-For converting a Fisher projection to a Haworth projection, we will follow the following steps-
(i) You first need to number carbons and draw in the Fisher stereochemistry.

(ii) Now, rotate the molecule to $90{}^\circ $ in clockwise direction.

(iii) Next step is the bond rotation of ${{C}_{4}}$with ${{C}_{5}}$.

(iv) Last step is the closure of fischer projection forming a closed ring structure.

(2) In the next part of the question, we are asked to write Fisher projection of $\alpha -D$Ribulofuranose.

Note:
For D-sugars, the last carbon will end up at the top of the Haworth projection. For L-sugars, the last carbon will end up on the top of the Haworth projection. At ${{C}_{1}}$ for D-sugars, if the OH group is down then it is an alpha-anomer whereas if the OH group is up then it is a beta-anomer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




