
When $0.2M$ acetic acid is neutralized with $0.1M$ NaOH in $0.5$ liters of water, the resultant solution is slightly alkaline. Calculate the pH of the resulting solution given that ${K_a}$ for $C{H_3}COOH = 1.8 \times {10^{ - 5}}$
Answer
570k+ views
Hint:The reaction between acetic acid and sodium hydroxide produces sodium acetate and water. Calculate the amount of sodium acetate and water produced in this reaction and find the concentration of sodium acetate accordingly. Now calculate the value of hydrolysis constant or ${K_h}$ to find the pH value.
Complete step-by-step solution:The above reaction between acetic acid and sodium hydroxide can be written as follows.
$C{H_3}COOH + NaOH \rightleftarrows C{H_3}COONa + {H_2}O$
$0.2M$ of acetic acid would give $0.2M$ of sodium acetate and $0.5$ liters of water. So the concentration of sodium acetate would be $0.1mol{L^{ - 1}}$
Given to us the association constant of acetic acid as ${K_a} = 1.8 \times {10^{ - 5}}$
Let us write the association reaction for acetic acid $C{H_3}CO{O^ - } + {H_2}O \rightleftarrows C{H_3}COOH + O{H^ - }$
For the above equilibrium reaction, we can write the concentrations as:
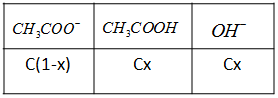
From this, we can write the value of hydrolysis constant as ${K_h} = \dfrac{{Cx \times Cx}}{{C\left( {1 - x} \right)}} = \dfrac{{C{x^2}}}{{1 - x}}$
Since the value of x is extremely small, we can approximate the value of $1 - x$ to be $1$ and hence the equation becomes ${K_h} = C{x^2}$
Now, we know that ${K_h} = \dfrac{{{K_w}}}{{{K_a}}}$ where ${K_w} = {10^{ - 14}}$ and the ${K_a}$ value is already given. By substituting these values, we get ${K_h} = \dfrac{{{{10}^{ - 14}}}}{{1.8 \times {{10}^{ - 5}}}} = 0.55 \times {10^{ - 9}}$
From this, we can write $C{x^2} = 0.55 \times {10^{ - 9}}$
We have already calculated the concentration as $0.1mol{L^{ - 1}}$ and by substituting this, we get ${x^2} = 5.5 \times {10^{ - 9}}$
This gives $x = 7.42 \times {10^{ - 5}}$
From the above table, the concentration of $O{H^ - }$ is $Cx = 0.1 \times 7.42 \times {10^{ - 5}} = 7.42 \times {10^{ - 6}}$
We know that the product of concentration of ${H^ + }$ and $O{H^ - }$ of a solution gives the value of dissociation constant of water.
$\left[ {{H^ + }} \right]\left[ {O{H^ - }} \right] = {K_w}$
From this, we can calculate the concentration of ${H^ + }$ as $\left[ {{H^ + }} \right] = \dfrac{{{K_w}}}{{\left[ {O{H^ - }} \right]}} = \dfrac{{{{10}^{ - 14}}}}{{7.42 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}}} = 1.347 \times {10^{ - 9}}M$
Now we can calculate the pH value as $ - \log \left[ {{H^ + }} \right] = 8.87$
Hence the pH value is $8.87$
Note: It is to be noted that we can also find the value of pOH first and derive the value of pH. This is because of the relation $pH + pOH = 14$ and hence the value of pH can be calculated. Therefore the pOH of this solution would be $14 - pH$ which is $14 - 8.87 = 5.13$ .
Complete step-by-step solution:The above reaction between acetic acid and sodium hydroxide can be written as follows.
$C{H_3}COOH + NaOH \rightleftarrows C{H_3}COONa + {H_2}O$
$0.2M$ of acetic acid would give $0.2M$ of sodium acetate and $0.5$ liters of water. So the concentration of sodium acetate would be $0.1mol{L^{ - 1}}$
Given to us the association constant of acetic acid as ${K_a} = 1.8 \times {10^{ - 5}}$
Let us write the association reaction for acetic acid $C{H_3}CO{O^ - } + {H_2}O \rightleftarrows C{H_3}COOH + O{H^ - }$
For the above equilibrium reaction, we can write the concentrations as:

From this, we can write the value of hydrolysis constant as ${K_h} = \dfrac{{Cx \times Cx}}{{C\left( {1 - x} \right)}} = \dfrac{{C{x^2}}}{{1 - x}}$
Since the value of x is extremely small, we can approximate the value of $1 - x$ to be $1$ and hence the equation becomes ${K_h} = C{x^2}$
Now, we know that ${K_h} = \dfrac{{{K_w}}}{{{K_a}}}$ where ${K_w} = {10^{ - 14}}$ and the ${K_a}$ value is already given. By substituting these values, we get ${K_h} = \dfrac{{{{10}^{ - 14}}}}{{1.8 \times {{10}^{ - 5}}}} = 0.55 \times {10^{ - 9}}$
From this, we can write $C{x^2} = 0.55 \times {10^{ - 9}}$
We have already calculated the concentration as $0.1mol{L^{ - 1}}$ and by substituting this, we get ${x^2} = 5.5 \times {10^{ - 9}}$
This gives $x = 7.42 \times {10^{ - 5}}$
From the above table, the concentration of $O{H^ - }$ is $Cx = 0.1 \times 7.42 \times {10^{ - 5}} = 7.42 \times {10^{ - 6}}$
We know that the product of concentration of ${H^ + }$ and $O{H^ - }$ of a solution gives the value of dissociation constant of water.
$\left[ {{H^ + }} \right]\left[ {O{H^ - }} \right] = {K_w}$
From this, we can calculate the concentration of ${H^ + }$ as $\left[ {{H^ + }} \right] = \dfrac{{{K_w}}}{{\left[ {O{H^ - }} \right]}} = \dfrac{{{{10}^{ - 14}}}}{{7.42 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}}} = 1.347 \times {10^{ - 9}}M$
Now we can calculate the pH value as $ - \log \left[ {{H^ + }} \right] = 8.87$
Hence the pH value is $8.87$
Note: It is to be noted that we can also find the value of pOH first and derive the value of pH. This is because of the relation $pH + pOH = 14$ and hence the value of pH can be calculated. Therefore the pOH of this solution would be $14 - pH$ which is $14 - 8.87 = 5.13$ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




