
$ ( + ) - $ Mandelic acid has a specific rotation of $ + {158^o} $ . What would be the observed specific rotation of a mixture of $ 25\% \;\left( - \right) - \; $ mandelic acid and $ 75\% \left( + \right) - \; $ mandelic acid:
Answer
500.4k+ views
Hint: Mandelic acid is aromatic in nature and is alpha hydroxy acid. It has a molecular formula $ {C_6}{H_5}CH\left( {OH} \right)C{O_2}H $ . It is a chiral molecule and its racemic mixture is known as para mandelic acid. Specific rotation is a property of a chemical compound which is chiral in nature. Now, we will find the observed specific rotation for the mandelic acid.
Complete answer:
So, now we know that Mandelic acid is aromatic in nature and is alpha hydroxy acid. It has a molecular formula $ {C_6}{H_5}CH\left( {OH} \right)C{O_2}H $ . Its structure is:
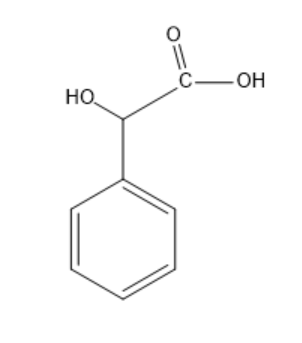
So we can clearly see that it is a chiral molecule and hence, shows specific rotation.
Specific rotation is defined as the change in the orientation of a monochromatic plane-polarized light as it passes through a sample of compound in the solution.
Formula used to find observed specific rotation is given as:
$ E.E = \dfrac{{[\alpha ]}}{{\alpha (pure( + )enantiomer)}} $
Here, E.E refers to enantiomeric excess.
$ [\alpha ] $ is the observed specific rotation.
$ \alpha $ is the specific rotation of pure $ ( + ) - $ Mandelic acid.
So, now we are given with:
Concentration of $ \;\left( - \right) - \; $ mandelic acid is $ 25\% $ .
Concentration of $ ( + ) - $ Mandelic acid is $ 75\% $ .
Enantiomeric excess of $ ( + ) - $ Mandelic acid is $ 75 - 25 $
$ = 50\% $
Putting these values in the formula, we get:
$ 50 = \dfrac{{[\alpha ]}}{{158}} \times 100\% $
$ [\alpha ] = + {79^o} $
Therefore, the observed specific rotation of the mixture is, $ [\alpha ] = + {79^o} $ .
Note :
Chiral compounds are those compounds in which at least one carbon atom is chiral (have four different groups attached to it). Chiral compounds can rotate monochromatic plane-polarized light. Achiral molecules are those in which there is no chiral carbon present and this type of molecule is not able to rotate the plane-polarized light.
Complete answer:
So, now we know that Mandelic acid is aromatic in nature and is alpha hydroxy acid. It has a molecular formula $ {C_6}{H_5}CH\left( {OH} \right)C{O_2}H $ . Its structure is:

So we can clearly see that it is a chiral molecule and hence, shows specific rotation.
Specific rotation is defined as the change in the orientation of a monochromatic plane-polarized light as it passes through a sample of compound in the solution.
Formula used to find observed specific rotation is given as:
$ E.E = \dfrac{{[\alpha ]}}{{\alpha (pure( + )enantiomer)}} $
Here, E.E refers to enantiomeric excess.
$ [\alpha ] $ is the observed specific rotation.
$ \alpha $ is the specific rotation of pure $ ( + ) - $ Mandelic acid.
So, now we are given with:
Concentration of $ \;\left( - \right) - \; $ mandelic acid is $ 25\% $ .
Concentration of $ ( + ) - $ Mandelic acid is $ 75\% $ .
Enantiomeric excess of $ ( + ) - $ Mandelic acid is $ 75 - 25 $
$ = 50\% $
Putting these values in the formula, we get:
$ 50 = \dfrac{{[\alpha ]}}{{158}} \times 100\% $
$ [\alpha ] = + {79^o} $
Therefore, the observed specific rotation of the mixture is, $ [\alpha ] = + {79^o} $ .
Note :
Chiral compounds are those compounds in which at least one carbon atom is chiral (have four different groups attached to it). Chiral compounds can rotate monochromatic plane-polarized light. Achiral molecules are those in which there is no chiral carbon present and this type of molecule is not able to rotate the plane-polarized light.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




