




Step-by-Step Guide: Plotting Integers and Solving Examples
Integers are a set of positive and whole numbers including 0. A number line is a visual representation of numbers on a straight line. This line is used to compare numbers that are placed at equal intervals on an infinite line that extends on both sides, horizontally or vertically. It’s a helpful tool for students wanting to learn the number system. This article will help you master the number line and may help you in your number line project.
What is the Number Line?
A one-dimensional graph of a line in which integers are shown as specially marked dots that are evenly spaced is called a number line. It is divided into two symmetrical halves by the origin, the number zero.
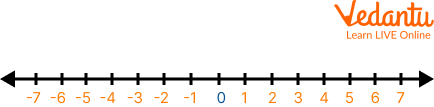
Number Line
Set of Integers
Integers are the set of numbers formed by all natural numbers (positive numbers) by zero and by negative numbers (those that are smaller than zero and have a minus sign in front)
The natural numbers: $1,2,3,4,5,6,7 \cdots$ so on to infinity ( $\infty$ ) are the positive numbers. They could be written as $+1,+2,+3,+4,+5, \ldots$.
The zero: 0 (It is neither positive nor negative, it is neutral)
The negative numbers: $-1,-2,-3,-4,-5,-6,-7 \ldots$ so on to minus infinity $(-\infty)$
You may ask yourself, are the numbers natural numbers or integers?
Well, it is inside the two sets because they belong to the natural numbers, but this set is contained in the integers. So, in other words, the natural numbers are a subset of the integers.
The set of integers is represented by the letter $Z$:
$Z=\{\ldots-6,-5,-4,-3,-2,-1,0,1,2,3,4,5,6 \ldots\}$
How to Represent Integers on a Number Line?
The representation of integers on number line is done in the following way:
1. We draw the line, divide into equal parts and put 0 in the centre.

A Line
2. We place the positive numbers to the right of zero, increasing their value by one unit, from left to right.
3. Now we place the negative numbers to the left of zero. They all have a minus sign in front of them.
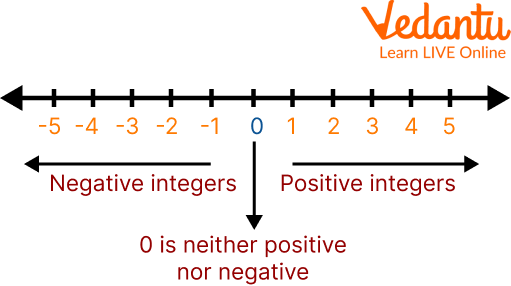
The Number Line
This can be clearly understood with the help of a number line. Now, after seeing how to represent integers on the number line, we are going to see how they are ordered.
Number Line Addition and Subtraction of Integers
Now that we understand how to add and subtract integers on a number line of integers, we can learn other arithmetic operations. To add a positive number means that we move the point to the right of the number line. Similarly, to add a negative number implies that we move the point to the left of the number line.
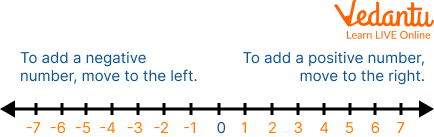
Number Line Addition and Subtraction of Integers
Multiplication of Integers on Number Line
The application of a multiplication operation on a given set of integers on a number line is known as multiplication of integers on a number line. Repeated addition is another name for multiplication. To conduct multiplication on a number line, we begin at zero and work our way to the right side of the number line for a certain number of times. Consider the following example. Using a number line, multiply 3 5 times.
On the number line, three sets of five identical intervals must be made beginning at zero. We will achieve 15 by organising three separate groups. Consider the following number line: 3 x 5 = 15.
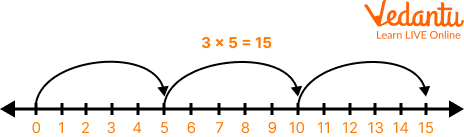
Multiplication of Numbers on Number Line
Now let’s see some number line examples.
Solved Examples
Q 1. Perform the operation 3 + (-4) using a number line.
Ans:
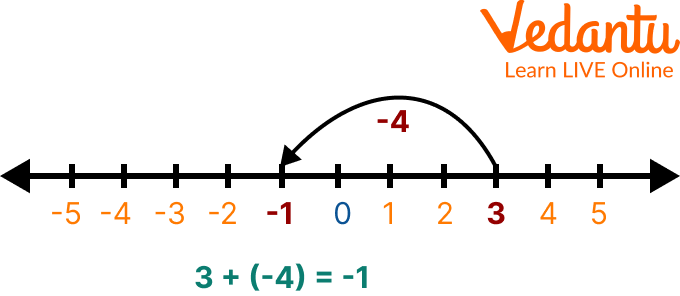
Addition on Number Line
Here, since the second number is $-4$ and the result is $-1$, we start with 3 and move 4 units to the left on the number line.
Q 2. How will you operate 7 + 12 using a number line? Explain in words.
Ans: The number 7 is marked on the number line. From there, we will proceed 12 units to the right on the number line, where we will eventually arrive at 19.
As a result, we use a number line to calculate 7 + 12 = 19.
Q 3. Add -5 and -2 using the number line.
Ans: Here, the first number is -5 and the second number is -2; both are negative. Locate -2 on the number line. Then moving 5 places to the left will give -7.
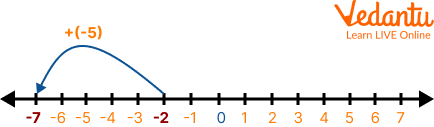
Addition on Number Line
Q 4. Subtract 5 from 2 using the number line
Ans: Here the first number is 2 and the second number is 5; both are positive. First, locate 2 on the number line. Then moving 5 places to the left will give us -3.
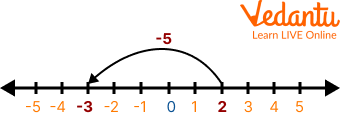
Subtraction on Number Line
Practice Questions
Q 1. When -2 is added to 8, keeping 8 as the reference, we move by ____ on the number line.
Ans: 2 units towards the left
Q 2. Which way do we move on the number line when we add a positive number?
Ans: Right of the number line
Q 3. Which way do the negative numbers are placed to the zero?
Ans: To the left
Q 4. Which way do the positive numbers lie to the zero?
Ans: To the right
Q 5. The addition of 8 and 1 in the number line is____
Ans: 9
Summary
Integers are plotted on a number line by adhering to the following fundamental guidelines: all positive numbers higher than zero, like $1,2,3, \ldots$, etc., are plotted to the right of zero, while all negative integers less than zero, like, $-1,-2,-3, \ldots$ etc., are plotted to the left of zero. The integer zero is precisely displayed in the middle. As an illustration, the integer 3 is plotted to the right of 0 , whereas the value $-4$ is drawn to the left of 0.
FAQs on How to Represent Integers on a Number Line
1. What are the essential steps to represent integers on a number line?
To represent integers on a number line, you must follow these key steps:
- Draw a horizontal straight line.
- Mark a point in the centre and label it as zero (0). This point is called the origin.
- Mark equally spaced points on the right side of zero and label them with positive integers (1, 2, 3, ...).
- Mark equally spaced points on the left side of zero and label them with negative integers (-1, -2, -3, ...).
2. How is addition of integers performed on a number line? For example, how to show (+4) + (-7)?
To perform addition on a number line, you start at the first integer and move based on the second integer. For (+4) + (-7):
- First, locate the integer +4 on the number line.
- Since you are adding a negative integer (-7), you must move 7 units to the left from +4.
- Moving 7 units to the left from +4 will land you on -3. Therefore, (+4) + (-7) = -3.
The rule is: to add a positive integer, move right; to add a negative integer, move left.
3. How does the number line help in comparing integers? For example, why is -6 smaller than -1?
A number line provides a clear visual method for comparing integers. The fundamental rule is: any integer on the right is always greater than any integer on its left. In the case of -6 and -1:
- Locate both -6 and -1 on the number line.
- You will observe that -1 is located to the right of -6.
- Therefore, -1 is greater than -6, or conversely, -6 is smaller than -1. This principle holds true for all integers.
4. What is the process for subtracting integers on a number line, such as 3 - (+5)?
Subtracting an integer on a number line means moving in the opposite direction of what you would for addition. To solve 3 - (+5):
- Start at the first integer, which is 3.
- To subtract a positive integer (+5), you must move 5 units to the left.
- Moving 5 units to the left from 3 brings you to -2. So, 3 - 5 = -2.
The general rule is: to subtract a positive integer, move left; to subtract a negative integer, move right.
5. What is the primary difference between representing whole numbers and integers on a number line?
The primary difference lies in the set of numbers they include. A number line for whole numbers starts at 0 and extends infinitely only to the right, including 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on. In contrast, a number line for integers extends infinitely in both directions from 0. It includes positive integers (1, 2, 3, ...) to the right, negative integers (-1, -2, -3, ...) to the left, and zero itself in the centre.
6. How does a number line visually explain why subtracting a negative integer is equivalent to adding a positive one?
The number line demonstrates this concept through movement. Subtracting means doing the 'opposite' of adding. For example, consider 2 - (-4):
- Adding a negative number (-4) means moving 4 units to the left.
- Therefore, subtracting a negative number (-4) must mean doing the opposite: moving 4 units to the right.
- Starting at 2 and moving 4 units to the right lands you on 6.
This is the exact same action as performing 2 + (+4). The number line shows that both operations result in the same final position, visually proving that 2 - (-4) = 2 + 4.
7. What is the concept of 'additive inverse,' and how is it identified on a number line?
The additive inverse of an integer is another integer that, when added to the first, results in a sum of zero. On a number line, the additive inverse of any non-zero integer is the integer that is the same distance from zero but on the opposite side. For example:
- The integer 5 is 5 units to the right of zero.
- Its additive inverse, -5, is 5 units to the left of zero.
- Adding them on the number line (starting at 5 and moving 5 units left) brings you back to 0.
8. Can you provide a real-world example where representing integers on a number line is useful?
A perfect real-world example is a thermometer measuring temperature in degrees Celsius or Fahrenheit. A thermometer is essentially a vertical number line.
- The freezing point of water, 0°C, acts as the origin.
- Temperatures above freezing are represented by positive integers (e.g., +10°C, +25°C).
- Temperatures below freezing are represented by negative integers (e.g., -5°C, -15°C).
This representation helps us easily compare temperatures and understand changes like a temperature drop from +2°C to -3°C, which is a move of 5 units down the number line.























